The Impact of Rhythmic Physical Activity on Mental Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults with and without Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38002696
- PMCID: PMC10672098
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12227084
The Impact of Rhythmic Physical Activity on Mental Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults with and without Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
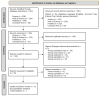
(1) Background: Nowadays, it is essential to implement new non-pharmacological strategies, such as rhythmic physical activity, to improve mental health and quality of life in both individuals experiencing normal brain aging and those with cognitive impairment. Therefore, the objective of this study is to identify the effects of rhythmic physical activity interventions on mental health and quality of life in older adults, with or without mild cognitive impairment; (2) Methods: We conducted a systematic review with a meta-analysis, searching the Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Plus databases using specific keywords. We selected studies that included rhythmic physical activity as the primary intervention for patients aged 65 and above, with or without cognitive impairment. We assessed the methodological quality of the articles using the PEDro scale; (3) Results: Out of 961 identified studies, we included 11 in this review, all of which employed rhythmic physical activity as an intervention. The selected studies consistently measured depression, anxiety, and quality of life; (4) Conclusions: This review demonstrates that rhythmic physical activity can effectively improve depression, anxiety, and quality of life in older adults, whether or not they have mild cognitive impairment. However, it is worth noting that while we have identified beneficial outcomes, the evidence supporting the use of rhythmic physical activity in enhancing depression, anxiety, and quality of life in older adults with or without mild cognitive impairment remains somewhat limited.
Keywords: dance; mental health; meta-analysis; older adults; quality of life; rhythmic; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
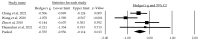
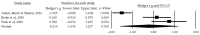
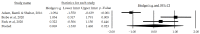
Similar articles
-
Effect of Dancing Interventions on Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/bs14010043. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dance therapy on cognitive and mental health in adults aged 55 years and older with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Geriatr. 2023 Oct 26;23(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04406-y. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37880590 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dance-Based Aerobic Training on Mental Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment.J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 9;14(8):844. doi: 10.3390/jpm14080844. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39202035 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dance Interventions on Cognition, Psycho-Behavioral Symptoms, Motor Functions, and Quality of Life in Older Adult Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Sep 20;13:706609. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.706609. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34616285 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exercise effects on neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life in mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 14;15:1447734. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1447734. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39469070 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between sex, age, BMI, health-related quality of life, and coping strategies in amateur and professional athletes.Front Physiol. 2025 Jun 24;16:1626037. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1626037. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40630392 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Dancing Interventions on Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/bs14010043. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Evidence Profile: Cognitive Impairment. 2017. [(accessed on 21 July 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/ageing/health-systems/icope/evidence-centre/ICOPE-ev....
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on the Public Health Response to Dementia. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

