Effects of COVID-19 Infection on Spermatogenesis, Oxidative Stress and Erectile Function
- PMID: 38002711
- PMCID: PMC10672023
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12227099
Effects of COVID-19 Infection on Spermatogenesis, Oxidative Stress and Erectile Function
Abstract
Background: Our aim was to evaluate the effect of COVID-19 infection on male fertility and sexual function.
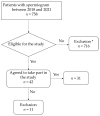
Methods: Thirty-one patients were investigated over a mean follow-up of 90 days (22-527) after a COVID-19 infection. Erectile dysfunction (ED), blood tests for sexual hormones, semen analysis including analysis of oxidative stress (OS), as well as COVID-19 antibody titer and the nasal COVID-19 PCR test were evaluated pre- and post-infection.
Results: Five patients reported a mild de novo ED (16.13%). One patient had a de novo positive mixed antiglobulin reaction test after the infection. We found no significant difference between pre-COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 spermiogram parameters (p = 0.815). OS showed no significant association with COVID-19 infection, but with pathological spermiogram categories, sperm concentration, total sperm count, testis volume, FSH and testosterone.
Conclusion: COVID-19 infection does not appear to affect sperm quality and OS negatively in the intermediate term. Further investigations will be needed to assess the potential long-term effects of the infection and vaccination on male sexual function and fertility.
Keywords: COVID-19; infection; male fertility; oxidative stress; semen analysis; testosterone; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Kruger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

