Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 38002786
- PMCID: PMC10672082
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12227174
Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
Background: Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor (VWF) are significantly elevated in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, dynamic changes and prognostic value of this biomarker in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 have not been determined.
Methods: A total of 124 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 were prospectively recruited for the study. Serial blood samples were obtained at the time of admission (D1), 3-4 days following standard-care treatments (D2), and 1-2 days prior to discharge or any time collected prior to death (D3). Plasma VWF antigen, ADAMTS13 antigen, and ADAMTS13 proteolytic activity, as well as the ratio of VWF/ADAMTS13 were determined, followed by various statistical analyses.
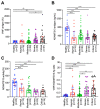
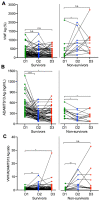
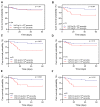
Results: On admission, plasma levels of VWF in COVID-19 patients were significantly elevated compared with those in the healthy controls, but no statistical significance was detected among patients with different disease severity. Plasma ADAMTS13 activity but not its antigen levels were significantly lower in patients with severe or critical COVID-19 compared with that in other patient groups. Interestingly, the ratios of plasma VWF antigen to ADAMTS13 antigen were significantly higher in patients with severe or critical COVID-19 than in those with mild to moderate disease. More importantly, plasma levels of VWF and the ratios of VWF/ADAMTS13 were persistently elevated in patients with COVID-19 throughout hospitalization. Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazard regression analyses demonstrated that an increased plasma level of VWF or ratio of VWF/ADAMTS13 at D2 and D3 was associated with an increased mortality rate.
Conclusions: Persistent endotheliopathy, marked by the elevated levels of plasma VWF or VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio, is present in all hospitalized patients following SARS-CoV-2 infection, which is strongly associated with mortality.
Keywords: ADAMTS13; COVID-19; endothelial dysfunction; mortality; von Willebrand factor.
Conflict of interest statement
X.L.Z. is a consultant for Alexion, Apollo, Argenx, BioMedica Diagnostics, GC Biopharma, Kyowa Kirin, Sanofi, and Takeda, as well as a co-founder of Clotsolution. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Von Willebrand factor collagen-binding capacity predicts in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: insight from VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio imbalance.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):407-411. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09789-3. Epub 2021 May 11. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33974165 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the von Willebrand Factor-ADAMTS13 Axis, Complement Activation, and COVID-19 Severity and Mortality.Thromb Haemost. 2022 Feb;122(2):240-256. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1740182. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35062036 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of convalescent plasma infusion on the ADAMTS13-von Willebrand factor axis and endothelial integrity in patients with severe and critical COVID-19.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 Jan;7(1):100010. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2022.100010. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36531671 Free PMC article.
-
Insights Into Immunothrombosis: The Interplay Among Neutrophil Extracellular Trap, von Willebrand Factor, and ADAMTS13.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 2;11:610696. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610696. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33343584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 microthrombosis: unusually large VWF multimers are a platform for activation of the alternative complement pathway under cytokine storm.Int J Hematol. 2022 Apr;115(4):457-469. doi: 10.1007/s12185-022-03324-w. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Int J Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35316498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease with Thrombospondin Motif, Member 13, and Von Willebrand Factor in Relation to the Duality of Preeclampsia and HIV Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4103. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094103. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Utility of Recently Food and Drug Administration-Approved IntelliSep Test (Sepsis Biomarker) for Early Diagnosis of Sepsis: Comparison with Other Biomarkers.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 16;13(16):4852. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164852. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200994 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a activates the endothelium to release von Willebrand factor that promotes thrombosis.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2025 Jun 20;9(4):102947. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2025.102947. eCollection 2025 May. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 40697485 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Endothelial Damage and Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 May 31;47(6):409. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060409. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699808 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Vascular Biomarkers for Predicting In-Hospital Mortality in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 22;12(1):229. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010229. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38276214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ortigoza M.B., Yoon H., Goldfeld K.S., Troxel A.B., Daily J.P., Wu Y., Li Y., Wu D., Cobb G.F., Baptiste G., et al. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma in Hospitalized Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022;182:115–126. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6850. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kutsogiannis D.J., Alharthy A., Balhamar A., Faqihi F., Papanikolaou J., Alqahtani S.A., Memish Z.A., Brindley P.G., Brochard L., Karakitsos D. Mortality and Pulmonary Embolism in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome From COVID-19 vs. Non-COVID-19. Front. Med. 2022;9:800241. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.800241. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

