Impact of a Web-Based Nutrition Intervention on Eating Behaviors and Body Size Preoccupations among Adolescents
- PMID: 38002827
- PMCID: PMC10670448
- DOI: 10.3390/children10111736
Impact of a Web-Based Nutrition Intervention on Eating Behaviors and Body Size Preoccupations among Adolescents
Abstract
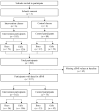
We aimed to evaluate the impact of a web-based school nutrition intervention on eating behavior traits, body weight concern, body size perception and body size dissatisfaction in adolescents. Ten classes of secondary students in Canada (13.6 ± 0.8 years) were randomized into an intervention (n = 162 students) or control group (n = 75 students). Adolescents in the intervention, conducted between 2011 and 2013, participated in an online nutrition challenge to increase their consumption of vegetables, fruits and dairy products using a web-based platform over six weeks. Measurements were taken at baseline (PRE) and post-intervention (POST). No significant negative changes were observed between the intervention and control groups for eating behavior traits, body weight concern, body size perception and dissatisfaction. However, results suggest a trend for a positive effect of the intervention on susceptibility to hunger in boys (group × time interaction, p = 0.10). Specifically, boys experienced a reduction in their susceptibility to hunger in response to the intervention (PRE: 6.1 ± 3.8, POST: 4.8 ± 3.7, p = 0.009). An intervention aimed at improving the eating habits of adolescents did not negatively influence body size preoccupations. In response to the intervention, boys tended to show a lower susceptibility to hunger, which might help them to prevent overeating and adopt healthy eating habits.
Keywords: adolescents; body size dissatisfaction; body size perception; eating behavior traits; nutrition intervention; weight preoccupation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of an innovative web-based school nutrition intervention to increase fruits and vegetables and milk and alternatives in adolescents: a clustered randomized trial.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017 Oct 16;14(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12966-017-0595-7. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017. PMID: 29037203 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Multi-Strategy Nutrition Education Programs on Hedonic Hunger and Nutrition Status in Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;11(10):1188. doi: 10.3390/children11101188. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457153 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of a family web-based nutrition intervention to increase fruit, vegetable, and dairy intakes: a single-blinded randomized family clustered intervention.Nutr J. 2022 Dec 20;21(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12937-022-00825-6. Nutr J. 2022. PMID: 36539753 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Body Image Concerns and Body Weight Overestimation Do Not Promote Healthy Behaviour: Evidence from Adolescents in Lithuania.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Mar 9;16(5):864. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16050864. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30857295 Free PMC article.
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Daily Optional Physical Education Does Not Counteract Increasing Inactivity by Age among Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;10(12):1929. doi: 10.3390/children10121929. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duncanson K., Shrewsbury V., Burrows T., Chai L.K., Ashton L., Taylor R., Gow M., Ho M., Ells L., Stewart L., et al. Impact of weight management nutrition interventions on dietary outcomes in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021;34:147–177. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12831. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Traoré I., Julien D., Camirand H.L.N., Street M.-C., Flores J. L’Enquête Québécoise sur la Santé des Jeunes du Secondaire 2016–2017. Résultats de la Deuxième Édition; Institut de la Statistique du Québec; Québec, QC, Canada: 2018.
-
- Duarte L.S., Palombo C.N.T., Solis-Cordero K., Kurihayashi A.Y., Steen M., Borges A.L.V., Fujimori E. The association between body weight dissatisfaction with unhealthy eating behaviors and lack of physical activity in adolescents: A systematic review. J. Child. Health Care. 2021;25:44–68. doi: 10.1177/1367493520904914. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharpe H., Griffiths S., Choo T.-H., Eisenberg M.E., Mitchison D., Wall M., Neumark-Sztainer D. The relative importance of dissatisfaction, overvaluation and preoccupation with weight and shape for predicting onset of disordered eating behaviors and depressive symptoms over 15 years. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018;51:1168–1175. doi: 10.1002/eat.22936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources