Managing Dental Phobia in Children with the Use of Virtual Reality: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature
- PMID: 38002854
- PMCID: PMC10670820
- DOI: 10.3390/children10111763
Managing Dental Phobia in Children with the Use of Virtual Reality: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
Background: It is common today to encounter anxiety in patients facing dental treatment. Virtual reality (VR) is presented as a high-performing and innovative procedure because it can distract patients undergoing dental procedures or prepare them for such treatments. In addition, this meta-analysis has gathered evidence on VR and its ability to reduce dental anxiety in pediatric patients undergoing different treatments.
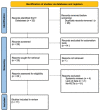
Methods: The major Scopus, PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science databases were searched for scientific articles published up to 2023. Studies in which VR was used for children and adults as a measure against anxiety during dental treatments were included. VR was defined as a three-dimensional place where patients experience a sense of immersion as they find themselves in attractive and interactive environments that detach them from reality. Anxiety and pain were examined and measured during dental treatments in which VR was used by comparing them with standard care situations.
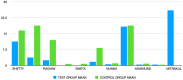
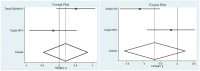
Results: Twenty-five studies were identified, of which eleven met the inclusion criteria. The effect of VR was studied mainly in the pediatric population as a distractive method. Only two studies (not significant) on an adult population were considered.
Conclusions: this review shows that VR is an excellent distraction method that is effective in reducing anxiety before dental treatment; however, due to the few studies in this area, further research on VR as a tool to prepare patients for dental treatment is needed.
Keywords: anxiety; behavior management; dental phobia; distraction systems; pain; pediatric dentistry; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Eijlers R., Utens E.M.W.J., Staals L.M., de Nijs P.F.A., Berghmans J.M., Wijnen R.M.H., Hillegers M.H.J., Dierckx B., Legerstee J.S. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Virtual Reality in Pediatrics: Effects on Pain and Anxiety. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2019;129:1344–1353. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

