Auditory Cortex Maturation and Language Development in Children with Hearing Loss and Additional Disabilities
- PMID: 38002904
- PMCID: PMC10670362
- DOI: 10.3390/children10111813
Auditory Cortex Maturation and Language Development in Children with Hearing Loss and Additional Disabilities
Abstract
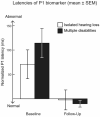
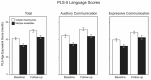
A significant portion of hearing-impaired children have additional disabilities, but data about the maturation of their auditory cortex are scarce. In these children, behavioral tests are often unreliable, and objective tests are needed for diagnostics and follow-up. This study aimed to explore auditory cortical maturation and language development, and the usability of an objective electroencephalogram-based biomarker in children with multiple disabilities. In 65 hearing aid and cochlear implant users (36 females; 36 with multiple disabilities; 44.3 ± 18.5 months of age, mean ± SD), auditory processing was examined using the P1 cortical auditory evoked response biomarker, and language development with the Preschool Language Scales 5th edition (PLS-5). During the study, all of the children received intensive extra language therapy for six months. No significant differences were found between the groups in P1 latency development, the proportion of abnormal P1 latencies, or the number of children whose P1 latencies changed from abnormal to normal during the study. The PLS-5 total language scores, auditory comprehension scores, or expressive communication scores did not differ between groups either. The P1 latencies showed meaningful negative correlations with the language scores. The results suggest that auditory cortex development is similar in hearing-impaired children with/without additional disabilities, and the P1 biomarker is a feasible tool to evaluate central auditory maturation in children with multiple disabilities.
Keywords: CAEP; EEG; P1 biomarker; auditory; cortical; disability; electroencephalogram; evoked potential; hearing loss; language.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Supplemental Language Therapy on Cortical Neuroplasticity and Language Outcomes in Children with Hearing Loss.Brain Sci. 2025 Jan 26;15(2):119. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020119. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002452 Free PMC article.
-
CENTRAL AUDTIORY DEVELOPMENT IN CHILDREN WITH HEARING LOSS: CLINICAL RELEVANCE OF THE P1 CAEP BIOMARKER IN HEARING-IMPAIRED CHILDREN WITH MULTIPLE DISABILITIES.Hearing Balance Commun. 2013 Sep;11(3):10.3109/21695717.2013.812378. doi: 10.3109/21695717.2013.812378. Hearing Balance Commun. 2013. PMID: 24273704 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Application of the P1 Cortical Auditory Evoked Potential Biomarker in Children with Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder.Semin Hear. 2011 May 1;32(2):147-155. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1277236. Semin Hear. 2011. PMID: 24078765 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical development and neuroplasticity in Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder.Hear Res. 2015 Dec;330(Pt B):221-32. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 26070426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental and cross-modal plasticity in deafness: evidence from the P1 and N1 event related potentials in cochlear implanted children.Int J Psychophysiol. 2015 Feb;95(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2014.04.007. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Int J Psychophysiol. 2015. PMID: 24780192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recommendations for selection of target parameters and process recommendations for audiological and technical functional testing of cochlear implant : Prepared by the ERA consortium (AG-ERA) of ADANO in cooperation with the Implantable Hearing Systems expert committee of the DGA. Confirmed by the board of ADANO on 31.01.2025.HNO. 2025 Jun 5. doi: 10.1007/s00106-025-01629-w. Online ahead of print. HNO. 2025. PMID: 40471261 Review. English.
-
The Role of Measuring Preoperative Social Maturation Score in Children With Additional Needs Who Underwent Cochlear Implantation.J Audiol Otol. 2024 Apr;28(2):107-113. doi: 10.7874/jao.2024.00101. Epub 2024 Apr 10. J Audiol Otol. 2024. PMID: 38695056 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Supplemental Language Therapy on Cortical Neuroplasticity and Language Outcomes in Children with Hearing Loss.Brain Sci. 2025 Jan 26;15(2):119. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020119. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002452 Free PMC article.
-
[Recommendations for selection of target parameters and process recommendations for audiological and technical functional testing of cochlear implant : Prepared by the ERA consortium (AG-ERA) of ADANO in cooperation with the Implantable Hearing Systems expert committee of the DGA. Confirmed by the board of ADANO on 31.01.2025. German version].HNO. 2025 Aug;73(8):550-557. doi: 10.1007/s00106-025-01628-x. Epub 2025 May 23. HNO. 2025. PMID: 40407893 Free PMC article. German.
References
-
- Home—OMIM. [(accessed on 1 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.omim.org/
-
- Shearer A.E., Hildebrand M.S., Schaefer A.M., Smith R.J. Genetic Hearing Loss Overview. In: Adam M.P., Mirzaa G.M., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., Bean L.J., Gripp K.W., Amemiya A., editors. GeneReviews®. University of Washington; Seattle, WA, USA: 1993. [(accessed on 1 October 2023)]. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1434/
-
- Cupples L., Ching T.Y.C., Button L., Leigh G., Marnane V., Whitfield J., Gunnourie M., Martin L. Language and speech outcomes of children with hearing loss and additional disabilities: Identifying the variables that influence performance at five years of age. Int. J. Audiol. 2018;57((Suppl. S2)):S93–S104. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2016.1228127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

