Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa
- PMID: 38003046
- PMCID: PMC10671189
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14112103
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa
Abstract
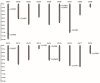
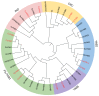
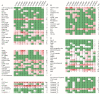
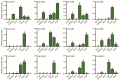
Plant-specific YABBY transcription factors play an important role in lateral organ development and abiotic stress responses. However, the functions of the YABBY genes in quinoa remain elusive. In this study, twelve YABBY (CqYAB) genes were identified in the quinoa genome, and they were distributed on nine chromosomes. They were classified into FIL/YAB3, YAB2, YAB5, INO, and CRC clades. All CqYAB genes consist of six or seven exons, and their proteins contain both N-terminal C2C2 zinc finger motifs and C-terminal YABBY domains. Ninety-three cis-regulatory elements were revealed in CqYAB gene promoters, and they were divided into six groups, such as cis-elements involved in light response, hormone response, development, and stress response. Six CqYAB genes were significantly upregulated by salt stress, while one was downregulated. Nine CqYAB genes were upregulated under drought stress, whereas six CqYAB genes were downregulated under cadmium treatment. Tissue expression profiles showed that nine CqYAB genes were expressed in seedlings, leaves, and flowers, seven in seeds, and two specifically in flowers, but no CqYAB expression was detected in roots. Furthermore, CqYAB4 could rescue the ino mutant phenotype in Arabidopsis but not CqYAB10, a paralog of CqYAB4, indicative of functional conservation and divergence among these YABBY genes. Taken together, these results lay a foundation for further functional analysis of CqYAB genes in quinoa growth, development, and abiotic stress responses.
Keywords: YABBY genes; abiotic stress; cis-elements; gene expression; quinoa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification of YABBY Genes in Orchidaceae and Their Expression Patterns in Phalaenopsis Orchid.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 19;11(9):955. doi: 10.3390/genes11090955. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825004 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SPL Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;13(8):1455. doi: 10.3390/genes13081455. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011366 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of YABBY transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon and functional characterization of Bd DROOPING LEAF.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Aug 15;185:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.05.030. Epub 2022 May 26. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35640497
-
Plant YABBY transcription factors: a review of gene expression, biological functions, and prospects.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2025 Feb;45(1):214-235. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2024.2344576. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38830825 Review.
-
Roles of YABBY transcription factors in the modulation of morphogenesis, development, and phytohormone and stress responses in plants.J Plant Res. 2020 Nov;133(6):751-763. doi: 10.1007/s10265-020-01227-7. Epub 2020 Oct 8. J Plant Res. 2020. PMID: 33033876 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of qPCR Reference Genes in Quinoa Under Cold, Heat, and Drought Gradient Stress.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;14(15):2434. doi: 10.3390/plants14152434. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pirzadah T.B., Malik B. Pseudocereals as super foods of 21st century: Recent technological interventions. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020;2:100052. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2020.100052. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

