Role and Regulation of Transcription Factors in Osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 38003376
- PMCID: PMC10671247
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216175
Role and Regulation of Transcription Factors in Osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
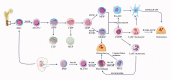
Bones serve mechanical and defensive functions, as well as regulating the balance of calcium ions and housing bone marrow.. The qualities of bones do not remain constant. Instead, they fluctuate throughout life, with functions increasing in some situations while deteriorating in others. The synchronization of osteoblast-mediated bone formation and osteoclast-mediated bone resorption is critical for maintaining bone mass and microstructure integrity in a steady state. This equilibrium, however, can be disrupted by a variety of bone pathologies. Excessive osteoclast differentiation can result in osteoporosis, Paget's disease, osteolytic bone metastases, and rheumatoid arthritis, all of which can adversely affect people's health. Osteoclast differentiation is regulated by transcription factors NFATc1, MITF, C/EBPα, PU.1, NF-κB, and c-Fos. The transcriptional activity of osteoclasts is largely influenced by developmental and environmental signals with the involvement of co-factors, RNAs, epigenetics, systemic factors, and the microenvironment. In this paper, we review these themes in regard to transcriptional regulation in osteoclastogenesis.
Keywords: epigenetics; osteoclast; osteoclast differentiation; osteoclastogenesis; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Euphorbia factor L1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis by regulating cellular redox status and induces Fas-mediated apoptosis in osteoclast.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Nov;112:191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.030. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28774817
-
Trapidil, a platelet-derived growth factor antagonist, inhibits osteoclastogenesis by down-regulating NFATc1 and suppresses bone loss in mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 15;86(6):782-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23928189
-
Lumichrome inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption through suppressing RANKL-induced NFAT activation and calcium signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Nov;233(11):8971-8983. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26841. Epub 2018 Jun 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29904917
-
Stimuli and Relevant Signaling Cascades for NFATc1 in Bone Cell Homeostasis: Friend or Foe?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(3):239-243. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666181205122729. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30516111
-
Regulation of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption by microRNA.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 May 10;79(6):287. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04298-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35536437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates platelet-rich plasma composition and accelerates bone healing.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 19;51:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.10.016. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 39902098 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast Activation and Inflammatory Bone Diseases: Focusing on Receptors in Osteoclasts.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 4;18:3201-3213. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S507269. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40059949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of the Role of Metabolic Features in Osteoporosis: A Multi-Omics Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2025 May 26;18:2727-2739. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S515717. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40453197 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Tanshinones in Osteolytic Diseases: From Molecular and Cellular Pathways to Preclinical Models.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;13(7):309. doi: 10.3390/dj13070309. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in the Battle Against Bone Metastases: Mechanisms and Emerging Treatments.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;17(12):1591. doi: 10.3390/ph17121591. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

