Advances in Intercellular Communication Mediated by Exosomal ncRNAs in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 38003385
- PMCID: PMC10671547
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216197
Advances in Intercellular Communication Mediated by Exosomal ncRNAs in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
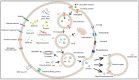
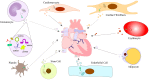
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of worldwide mortality, and exosomes have recently gained attention as key mediators of intercellular communication in these diseases. Exosomes are double-layered lipid vesicles that can carry biomolecules such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, and the content of exosomes is dependent on the cell they originated from. They can be involved in the pathophysiological processes of cardiovascular diseases and hold potential as diagnostic and monitoring tools. Exosomes mediate intercellular communication, stimulate or inhibit the activity of target cells, and affect myocardial hypertrophy, injury and infarction, ventricular remodeling, angiogenesis, and atherosclerosis. Exosomes can be released from various types of cells, including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, platelets, adipocytes, immune cells, and stem cells. In this review, we highlight the communication between different cell-derived exosomes and cardiovascular cells, with a focus on the roles of RNAs. This provides new insights for further exploring targeted therapies in the clinical management of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; circRNAs; exosomes; intercellular communication; lncRNAs; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes and Exosomal Cargos: A Promising World for Ventricular Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Oct 4;17:4699-4719. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S377479. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36217495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose exosomal noncoding RNAs: Roles and mechanisms in metabolic diseases.Obes Rev. 2024 Jun;25(6):e13740. doi: 10.1111/obr.13740. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Obes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38571458 Review.
-
Exosomes Mediate the Intercellular Communication after Myocardial Infarction.Int J Med Sci. 2016 Feb 1;13(2):113-6. doi: 10.7150/ijms.14112. eCollection 2016. Int J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26941569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles and therapeutic potential of exosomal non-coding RNAs in microglia-mediated intercellular communication.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Feb 20;148:114049. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114049. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39823800 Review.
-
Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: Novel Regulators of Macrophage-Linked Intercellular Communication in Lung Cancer and Inflammatory Lung Diseases.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 15;13(3):536. doi: 10.3390/biom13030536. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal non-coding RNAs: key molecules in the diagnosis and treatment of coronary artery disease.PeerJ. 2025 Jun 10;13:e19352. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19352. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40520644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal non-coding RNAs in the regulation of bone metabolism homeostasis: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 11;11(2):e41632. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41632. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39911437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Research on Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomal miRNAs: A Pivotal Insight into Aging and Age-Related Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 24;14(11):1354. doi: 10.3390/biom14111354. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing biomarkers for post-surgical wound healing: A meta-analysis of exosome-based CircRNA in breast cancer recovery.Int Wound J. 2024 Feb;21(2):e14723. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14723. Int Wound J. 2024. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Apr;22(4):e70534. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70534. PMID: 38379248 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicular microRNAs and cardiac hypertrophy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 9;15:1444940. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1444940. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39850481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

