Quassinoids from Twigs of Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr and Their Anti-Parkinson's Disease Effect
- PMID: 38003386
- PMCID: PMC10671724
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216196
Quassinoids from Twigs of Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr and Their Anti-Parkinson's Disease Effect
Abstract
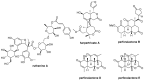
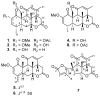
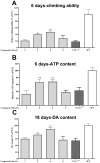
Six new C-20 and one new C-19 quassinoids, named perforalactones F-L (1-7), were isolated from twigs of Harrisonia perforata. Spectroscopic and X-ray crystallographic experiments were conducted to identify their structures. Through oxidative degradation of perforalactone B to perforaqussin A, the biogenetic process from C-25 quassinoid to C-20 via Baeyer-Villiger oxidation was proposed. Furthermore, the study evaluated the anti-Parkinson's disease potential of these C-20 quassinoids for the first time on 6-OHDA-induced PC12 cells and a Drosophila Parkinson's disease model of PINK1B9. Perforalactones G and I (2 and 4) showed a 10-15% increase in cell viability of the model cells at 50 μM, while compounds 2 and 4 (100 μM) significantly improved the climbing ability of PINK1B9 flies and increased the dopamine level in the brains and ATP content in the thoraces of the flies.
Keywords: Harrisonia perforata; PC12 cells; PINK1B9 flies; neuroprotection; quassinoid; simarubaceae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Perforalactones D and E, two new C-20 quassinoids with potential activity to induce lysosomal biogenesis from the twigs of Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Nov 18;19(44):9637-9640. doi: 10.1039/d1ob01927a. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34714900
-
Unprecedented Quassinoids with Promising Biological Activity from Harrisonia perforata.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 May 4;54(19):5592-5. doi: 10.1002/anie.201412126. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. PMID: 25810025
-
Harpertrioate A, an A,B,D-seco-Limonoid with Promising Biological Activity against Alzheimer's Disease from Twigs of Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.Org Lett. 2021 Jan 15;23(2):262-267. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03460. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Org Lett. 2021. PMID: 33284631
-
Quassinoids: From traditional drugs to new cancer therapeutics.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(3):316-28. doi: 10.2174/092986711794839205. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21143123 Review.
-
Quassinoids: Phytochemistry and antitumor prospect.Phytochemistry. 2021 Jul;187:112769. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112769. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Phytochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33887559 Review.
References
-
- Hipolith M.M., Khor B.K., Hirasawa Y., Murugaiyah V., Lee C.Y., Morita H., Wong P.F., Chan K.L. Quassinoids from Eurycoma longifolia Jack roots and their potential inhibitory activity against human benign prostatic hyperplasia cells (BPH-1) and testosterone-induced BPH rat model. Fitoterapia. 2023;166:105468. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105468. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31770392, T2192971/the natural science foundation of China
- 202201AS070040/the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- P2020-KF06/the Fund of State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China
- 2022ZYD0032/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- Yingtong Di/Plant Doctor project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

