MicroRNAs: Midfielders of Cardiac Health, Disease and Treatment
- PMID: 38003397
- PMCID: PMC10671258
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216207
MicroRNAs: Midfielders of Cardiac Health, Disease and Treatment
Abstract
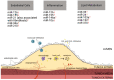
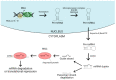
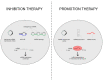
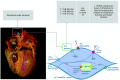
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNA molecules that play a role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. It is generally accepted that their main mechanism of action is the negative regulation of gene expression, through binding to specific regions in messenger RNA (mRNA) and repressing protein translation. By interrupting protein synthesis, miRNAs can effectively turn genes off and influence many basic processes in the body, such as developmental and apoptotic behaviours of cells and cardiac organogenesis. Their importance is highlighted by inhibiting or overexpressing certain miRNAs, which will be discussed in the context of coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and heart failure. Dysregulated levels of miRNAs in the body can exacerbate or alleviate existing disease, and their omnipresence in the body makes them reliable as quantifiable markers of disease. This review aims to provide a summary of miRNAs as biomarkers and their interactions with targets that affect cardiac health, and intersperse it with current therapeutic knowledge. It intends to succinctly inform on these topics and guide readers toward more comprehensive works if they wish to explore further through a wide-ranging citation list.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; biomarker; bradycardia; heart disease; heart failure; ion channels; miRNA; sinoatrial node.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

