Carnosine, Zinc and Copper: A Menage a Trois in Bone and Cartilage Protection
- PMID: 38003398
- PMCID: PMC10671046
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216209
Carnosine, Zinc and Copper: A Menage a Trois in Bone and Cartilage Protection
Abstract
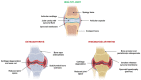
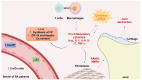
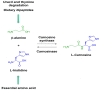
Dysregulated metal homeostasis is associated with many pathological conditions, including arthritic diseases. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two most prevalent disorders that damage the joints and lead to cartilage and bone destruction. Recent studies show that the levels of zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) are generally altered in the serum of arthritis patients. Therefore, metal dyshomeostasis may reflect the contribution of these trace elements to the disease's pathogenesis and manifestations, suggesting their potential for prognosis and treatment. Carnosine (Car) also emerged as a biomarker in arthritis and exerts protective and osteogenic effects in arthritic joints. Notably, its zinc(II) complex, polaprezinc, has been recently proposed as a drug-repurposing candidate for bone fracture healing. On these bases, this review article aims to provide an overview of the beneficial roles of Cu and Zn in bone and cartilage health and their potential application in tissue engineering. The effects of Car and polaprezinc in promoting cartilage and bone regeneration are also discussed. We hypothesize that polaprezinc could exchange Zn for Cu, present in the culture media, due to its higher sequestering ability towards Cu. However, future studies should unveil the potential contribution of Cu in the beneficial effects of polaprezinc.
Keywords: arthritis; bone; carnosine; cartilage; copper; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparison of the cellular actions of polaprezinc (zinc-L-carnosine) and ZnCl2.Life Sci. 2012 Jun 27;90(25-26):1015-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.05.017. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22683432
-
Zinc-L-Carnosine Complex (Polaprezinc) for the Treatment of Binge Eating: Three Case Reports.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2017 Dec;37(6):734-736. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000784. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28926352 No abstract available.
-
Drug repositioning of polaprezinc for bone fracture healing.Commun Biol. 2022 May 16;5(1):462. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03424-7. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35577977 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of polaprezinc research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(3):271-7. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.132.271. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22382829 Review. Japanese.
-
Zinc, Carnosine, and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Nutrients. 2018 Jan 29;10(2):147. doi: 10.3390/nu10020147. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29382141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Honeycomb-like biomimetic scaffold by functionalized antibacterial hydrogel and biodegradable porous Mg alloy for osteochondral regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 12;12:1417742. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1417742. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39070169 Free PMC article.
-
A Molecular Hybrid of the GFP Chromophore and 2,2'-Bipyridine: An Accessible Sensor for Zn2+ Detection with Fluorescence Microscopy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3504. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063504. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542479 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Isomeric TAT1-CARNOSINE Peptides by Energy-Resolved Mass Spectrometry and Principal Component Analysis.Molecules. 2025 Feb 12;30(4):853. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040853. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005164 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the Relationship Between Zinc and Copper in Patients with Osteoarthritis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Feb;203(2):635-645. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04197-2. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 38676877
-
Copper metabolism in osteoarthritis and its relation to oxidative stress and ferroptosis in chondrocytes.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Sep 11;11:1472492. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1472492. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39329090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rabiei M., Kashanian S., Samavati S.S., Derakhshankhah H., Jamasb S., McInnes S.J. Nanotechnology application in drug delivery to osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and osteoporosis (OSP) J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020;61:102011. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

