The Role of Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Human Placenta
- PMID: 38003402
- PMCID: PMC10671790
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216210
The Role of Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Human Placenta
Abstract
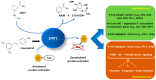
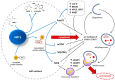
Sirtuins, especially SIRT1, play a significant role in regulating inflammatory response, autophagy, and cell response to oxidative stress. Since their discovery, sirtuins have been regarded as anti-ageing and longevity-promoting enzymes. Sirtuin-regulated processes seem to participate in the most prevalent placental pathologies, such as pre-eclampsia. Furthermore, more and more research studies indicate that SIRT1 may prevent pre-eclampsia development or at least alleviate its manifestations. Having considered this, we reviewed recent studies on the role of sirtuins, especially SIRT1, in processes determining normal or abnormal development and functioning of the placenta.
Keywords: PPARγ; SIRT1; SIRT1/PPARγ signaling; human placenta; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; placental pathophysiology; placental physiology; pre-eclampsia; sirtuin-1; sirtuins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

