Transcriptome Shock in Developing Embryos of a Brassica napus and Brassica rapa Hybrid
- PMID: 38003428
- PMCID: PMC10671433
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216238
Transcriptome Shock in Developing Embryos of a Brassica napus and Brassica rapa Hybrid
Abstract
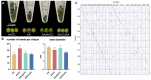
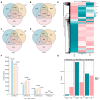
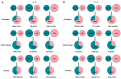
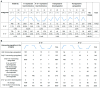
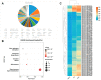
Interspecific crosses that fuse the genomes of two different species may result in overall gene expression changes in the hybrid progeny, called 'transcriptome shock'. To better understand the expression pattern after genome merging during the early stages of allopolyploid formation, we performed RNA sequencing analysis on developing embryos of Brassica rapa, B. napus, and their synthesized allotriploid hybrids. Here, we show that the transcriptome shock occurs in the developing seeds of the hybrids. Of the homoeologous gene pairs, 17.1% exhibit expression bias, with an overall expression bias toward B. rapa. The expression level dominance also biases toward B. rapa, mainly induced by the expression change in homoeologous genes from B. napus. Functional enrichment analysis revealed significant differences in differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to photosynthesis, hormone synthesis, and other pathways. Further study showed that significant changes in the expression levels of the key transcription factors (TFs) could regulate the overall interaction network in the developing embryo, which might be an essential cause of phenotype change. In conclusion, the present results have revealed the global changes in gene expression patterns in developing seeds of the hybrid between B. rapa and B. napus, and provided novel insights into the occurrence of transcriptome shock for harnessing heterosis.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; expression level dominance; homoeolog expression bias; transcriptome shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome shock in interspecific F1 allotriploid hybrids between Brassica species.J Exp Bot. 2022 Apr 18;73(8):2336-2353. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac047. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35139197
-
Homoeolog expression bias and expression level dominance in resynthesized allopolyploid Brassica napus.BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 6;19(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4966-5. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30081834 Free PMC article.
-
Homoeolog expression bias and expression level dominance (ELD) in four tissues of natural allotetraploid Brassica napus.BMC Genomics. 2020 Apr 29;21(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6747-1. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32349676 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression profiles of miRNAs in the triploid hybrids of Brassica napus and Brassica rapa.BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 14;20(1):649. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6001-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31412776 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecific Hybridization of Transgenic Brassica napus and Brassica rapa-An Overview.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 13;13(8):1442. doi: 10.3390/genes13081442. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kopecky D., Martin A., Smykal P. Interspecific hybridization and plant breeding: From historical retrospective through work of Mendel to current crops. Czech. J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2022;58:113–126. doi: 10.17221/19/2022-CJGPB. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

