GSK2656157, a PERK Inhibitor, Alleviates Pyroptosis of Macrophages Induced by Mycobacterium Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Infection
- PMID: 38003429
- PMCID: PMC10671627
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216239
GSK2656157, a PERK Inhibitor, Alleviates Pyroptosis of Macrophages Induced by Mycobacterium Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Infection
Abstract
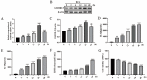
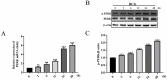
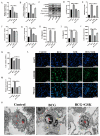
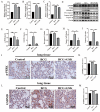
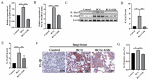
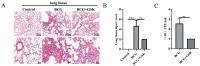
Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of human death worldwide due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. Mtb infection can cause macrophage pyroptosis. PERK, as a signaling pathway protein on the endoplasmic reticulum, plays an important role in infectious diseases. It is not clear whether PERK is involved in the regulation of pyroptosis of macrophages during Mtb infection. In this study, Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) infection resulted in high expression of pro-caspase-1, caspase-1 p20, GSDMD-N, and p-PERK in the THP-1 macrophage, being downregulated with the pre-treatment of GSK2656157, a PERK inhibitor. In addition, GSK2656157 inhibited the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, cell content release, and cell membrane rupture, as well as the decline in cell viability induced by BCG infection. Similarly, GSK2656157 treatment downregulated the expressions of pro-caspase-1, caspase-1 p20, caspase-11, IL-1β p17, IL-18 p22, GSDMD, GSDMD-N, and p-PERK, as well as reducing fibrous tissue hyperplasia, inflammatory infiltration, and the bacterial load in the lung tissue of C57BL/6J mice infected with BCG. In conclusion, the inhibition of PERK alleviated pyroptosis induced by BCG infection, which has an effect of resisting infection.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmette–Guerin; PERK; macrophages; pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis in THP-1 Macrophages Infected with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 20;24(14):11692. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411692. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511451 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates pyroptosis in macrophages infected with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin mycobacterial.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;152:114346. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114346. Epub 2025 Mar 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40064059
-
S100A4 Promotes BCG-Induced Pyroptosis of Macrophages by Activating the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 11;24(16):12709. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612709. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628889 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupled pyroptosis and IL-1β secretion downstream of inflammasome signaling.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1128358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128358. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37090724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens.Immunol Rev. 2015 May;265(1):130-42. doi: 10.1111/imr.12287. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25879289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glaesserella parasuis infection triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated pyroptosis via PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 axis and metabolic reprogramming in porcine alveolar macrophages.Vet Res. 2025 Jul 15;56(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01580-2. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40665414 Free PMC article.
-
The PERK/ATF4 pathway is required for metabolic reprogramming and progressive lung fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2025 Apr 10;10(10):e189330. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.189330. eCollection 2025 May 22. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40208691 Free PMC article.
-
Serine metabolism in macrophage polarization.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jan;73(1):83-98. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01815-y. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38070057 Review.
-
Pyroptosis in health and disease: mechanisms, regulation and clinical perspective.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 20;9(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01958-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39300122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

