New Derivatives of N- Hydroxybutanamide: Preparation, MMP Inhibition, Cytotoxicity, and Antitumor Activity
- PMID: 38003553
- PMCID: PMC10671431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216360
New Derivatives of N- Hydroxybutanamide: Preparation, MMP Inhibition, Cytotoxicity, and Antitumor Activity
Abstract
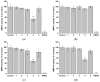
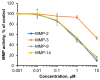
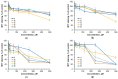
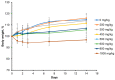
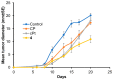
Using a novel method of N-substituted succinimide ring opening, new N-hydroxybutanamide derivatives were synthesized. These compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their cytotoxicity. The iodoaniline derivative of N1-hydroxy-N4-phenylbutanediamide showed the inhibition of MMP-2, MMP-9, and MMP-14 with an IC50 of 1-1.5 μM. All the compounds exhibited low toxicity towards carcinoma cell lines HeLa and HepG2. The iodoaniline derivative was also slightly toxic to glioma cell lines A-172 and U-251 MG. Non-cancerous FetMSC and Vero cells were found to be the least sensitive to all the compounds. In vivo studies demonstrated that the iodoaniline derivative of N1-hydroxy-N4-phenylbutanediamide had low acute toxicity. In a mouse model of B16 melanoma, this compound showed both antitumor and antimetastatic effects, with a 61.5% inhibition of tumor growth and an 88.6% inhibition of metastasis. Our findings suggest that the iodoaniline derivative of N1-hydroxy-N4-phenylbutanediamide has potential as a lead structure for the development of new MMP inhibitors. Our new synthetic approach can be a cost-effective method for the synthesis of inhibitors of metalloenzymes with promising antitumor potential.
Keywords: N-hydroxybutanamides; N-substituted succinimide ring opening method; acute toxicity; antimetastatic activity; antitumor activity; cytotoxicity; hydroxamic acids; matrix metalloproteinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
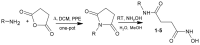



Similar articles
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of UTX-121 Derivatives for the Development of Novel Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Inhibitors.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021;69(10):1017-1028. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c21-00549. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 34602570
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of A New Series of Thiazole Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents and MMP Inhibitors.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(5):674-681. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160802113620. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27491937
-
Structure-based design and optimization of pyrimidine- and 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidine-based matrix metalloproteinase-10/13 inhibitors via Dimroth rearrangement towards targeted polypharmacology.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Mar;96:103616. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103616. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32032847
-
Targeting the interplay between MMP-2, CA II and VEGFR-2 via new sulfonamide-tethered isomeric triazole hybrids; Microwave-assisted synthesis, computational studies and evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Jul;124:105816. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105816. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35489270 Review.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Targeted Drug Delivery: Synthesis of a Potent and Highly Selective Inhibitor against Matrix Metalloproteinase- 7.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(27):2459-2471. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200722104928. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32703131 Review.
References
-
- Gupta S.P. Hydroxamic Acids. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2013.
-
- Ugwu D.I., Ezema B.E., Eze F.U., Ayogu J.I., Ezema C.G., Ugwuja D.I. Synthesis and Biological Applications of Hydroxamates. Am. J. Org. Chem. 2014;4:26–51. doi: 10.5923/j.ajoc.20140402.02. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

