ZNF643/ZFP69B Exerts Oncogenic Properties and Associates with Cell Adhesion and Immune Processes
- PMID: 38003570
- PMCID: PMC10671213
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216380
ZNF643/ZFP69B Exerts Oncogenic Properties and Associates with Cell Adhesion and Immune Processes
Abstract
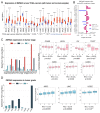
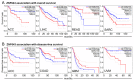
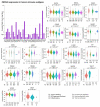
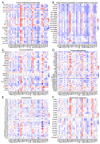
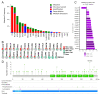
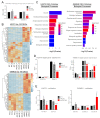
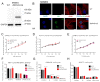
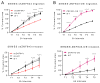
The global cancer burden remains high; thus, a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms driving carcinogenesis is needed to improve current prevention and treatment options. We previously detected the ZNF643/ZFP69B gene upregulated in multiple tumors, and we speculated it may play a role in tumor biology. To test this hypothesis, we employed TCGA-centered databases to correlate ZNF643 status with various clinicopathological parameters. We also performed RNA-seq analysis and in vitro studies assessing cancer cell phenotypes, and we searched for ZNF643-bound genomic loci. Our data indicated higher levels of ZNF643 in most analyzed tumors compared to normal samples, possibly due to copy number variations. ZNF643 mRNA correlated with diverse molecular and immune subtypes and clinicopathological features (tumor stage, grade, patient survival). RNA-seq analysis revealed that ZNF643 silencing triggers the deregulation of the genes implicated in various cancer-related processes, such as growth, adhesion, and immune system. Moreover, we observed that ZNF643 positively influences cell cycle, migration, and invasion. Finally, our ChIP-seq analysis indicated that the genes associated with ZNF643 binding are linked to adhesion and immune signaling. In conclusion, our data confirm the oncogenic properties of ZNF643 and pinpoint its impact on cell adhesion and immune processes.
Keywords: ChIP-seq; KRAB-ZFP; TCGA datasets; ZFP69B; ZNF643; oncogenes; transcriptomic profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive characterization of functional eRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma reveals novel regulators and a prognosis-related molecular subtype.Theranostics. 2020 Sep 14;10(24):11264-11277. doi: 10.7150/thno.47039. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33042282 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic Copy Number Alterations at Oncogenic Loci Show Diverse Correlations with Gene Expression.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 20;6:19649. doi: 10.1038/srep19649. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26787600 Free PMC article.
-
KRAB-ZFP Transcriptional Regulators Acting as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 23;22(4):2212. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042212. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression signature of cancer-associated KRAB-ZNF factors identified in TCGA pan-cancer transcriptomic data.Mol Oncol. 2019 Apr;13(4):701-724. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12407. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30444046 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of cell adhesion molecules in glioblastoma identified prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor (PTGFRN) as an essential gene.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 11;22(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09682-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35690717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression and clinicopathological significance of zinc finger protein 71 in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Hepatol. 2025 Feb 27;17(2):101914. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101914. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40027564 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of ZFP69B promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by upregulating the expression of TLX1 and TRAPPC9.Cell Div. 2024 Sep 11;19(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00131-z. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 39261946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

