Functional Dimerization of Serotonin Receptors: Role in Health and Depressive Disorders
- PMID: 38003611
- PMCID: PMC10671093
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216416
Functional Dimerization of Serotonin Receptors: Role in Health and Depressive Disorders
Abstract
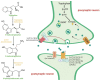
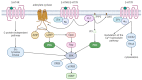
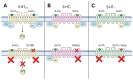
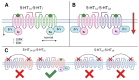
Understanding the neurobiological underpinnings of depressive disorder constitutes a pressing challenge in the fields of psychiatry and neurobiology. Depression represents one of the most prevalent forms of mental and behavioral disorders globally. Alterations in dimerization capacity can influence the functional characteristics of serotonin receptors and may constitute a contributing factor to the onset of depressive disorders. The objective of this review is to consolidate the current understanding of interactions within the 5-HT receptor family and between 5-HT receptors and members of other receptor families. Furthermore, it aims to elucidate the role of such complexes in depressive disorders and delineate the mechanisms through which antidepressants exert their effects.
Keywords: 5-HT; 5-HT receptors; depression; receptor dimerization; serotonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Developments on Future Antidepressant-related Serotonin Receptors.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(22):2541-2548. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180803111240. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30073919 Review.
-
Monoamine neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Aug 1;45:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23602950 Review.
-
Effects of serotonin in the hippocampus: how SSRIs and multimodal antidepressants might regulate pyramidal cell function.CNS Spectr. 2016 Apr;21(2):143-61. doi: 10.1017/S1092852915000425. Epub 2015 Sep 8. CNS Spectr. 2016. PMID: 26346726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mechanism of action of antidepressants and therapeutic perspectives].Therapie. 2002 Jul-Aug;57(4):385-96. Therapie. 2002. PMID: 12422559 Review. French.
-
Discovery of 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine (Lu AA21004): a novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder.J Med Chem. 2011 May 12;54(9):3206-21. doi: 10.1021/jm101459g. Epub 2011 Apr 12. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21486038
Cited by
-
Serotonin in depression and Alzheimer's disease: Focus on SSRI's beneficial effects.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Nov;101:102537. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102537. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39389238 Review.
-
Bifidobacterium breve BB05 alleviates depressive symptoms in mice via the AKT/mTOR pathway.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 30;12:1529566. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1529566. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39949541 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 5-HT4 receptor antagonist in the caudate nucleus on the performance of macaques in a delayed reward task.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70414-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39179718 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of 5-HT4 Receptors on Neuron-Glial Network Activity In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 9;26(16):7718. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167718. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869038 Free PMC article.
-
The psychedelic-peptide paradox: a hormetic hypothesis.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2025 Jun 2;23:100303. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2025.100303. eCollection 2025 Aug. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40584160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

