Pan-Inhibition of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Caused Cell Death through Disrupting Cellular Proteostasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 38003657
- PMCID: PMC10671009
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216467
Pan-Inhibition of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Caused Cell Death through Disrupting Cellular Proteostasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
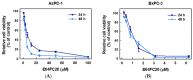
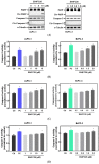
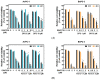
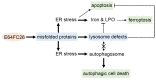
The protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) family is a group of thioredoxin endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident enzymes and molecular chaperones that play crucial roles in the correct folding of proteins. PDIs are upregulated in multiple cancer types and are considered a novel target for cancer therapy. In this study, we found that a potent pan-PDI inhibitor, E64FC26, significantly decreased the proliferation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells. As expected, E64FC26 treatment increased ER stress and the unfolded protein response (UPR), as evidenced by upregulation of glucose-regulated protein, 78-kDa (GRP78), phosphorylated (p)-PKR-like ER kinase (PERK), and p-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α). Persistent ER stress was found to lead to apoptosis, ferroptosis, and autophagy, all of which are dependent on lysosomal functions. First, there was little cleaved caspase-3 in E64FC26-treated cells according to Western blotting, but a higher dose of E64FC26 was needed to induce caspase activity. Then, E64FC26-induced cell death could be reversed by adding the iron chelator, deferoxamine, and the reactive oxygen species scavengers, ferrostatin-1 and N-acetylcysteine. Furthermore, the autophagosome-specific marker, light chain 3B (LC3B)-II, increased, but the autolysosome marker, sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1)/p62, was not degraded in E64FC26-treated cells. Using the FUW mCherry-LC3 plasmid and acridine orange staining, we also discovered a lower number of acidic vesicles, such as autolysosomes and mature lysosomes, in E64FC26-treated cells. Finally, E64FC26 treatment increased the cathepsin L precursor (pre-CTSL) but decreased mature CTSL expression according to Western blotting, indicating a defective lysosome. These results suggested that the PDI inhibitor, E64FC26, might initially impede proper folding of proteins, and then induce ER stress and disrupt proteostasis, subsequently leading to lysosomal defects. Due to defective lysosomes, the extents of apoptosis and ferroptosis were limited, and fusion with autophagosomes was blocked in E64FC26-treated cells. Blockade of autolysosomal formation further led to the autophagic cell death of PDAC cells.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; ferroptosis; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; protein disulfide isomerase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) negatively regulate ebolavirus structural glycoprotein expression in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the autophagy-lysosomal pathway.Autophagy. 2022 Oct;18(10):2350-2367. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2031381. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35130104 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors.Cells. 2019 Nov 26;8(12):1514. doi: 10.3390/cells8121514. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31779147 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress-mediated autophagy enhances the effectiveness of chemotherapeutics on pancreatic cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 Jul 9;16(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1562-z. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29986726 Free PMC article.
-
Structures and functions of protein disulfide isomerase family members involved in proteostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jun;83:314-22. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.02.010. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25697777 Review.
-
Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):583-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23567086 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the role of cathepsins in breast cancer progression: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 29;15:1408723. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1408723. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39944834 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA hsa_circ_0004781 promoted cell proliferation by acting as a sponge for miR-9-5p and miR-338-3p and upregulating KLF5 and ADAM17 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Feb 19;25(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03687-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 39972489 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-a key guardian in cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 30;10(1):343. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02110-3. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39080273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular signatures of disulfidptosis: interplay with programmed cell death pathways and therapeutic implications in oncology.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jun 2;30(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00743-5. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40457177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on ferroptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Mar 7;18:1359453. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1359453. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38515787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lukas J., Pospech J., Oppermann C., Hund C., Iwanov K., Pantoom S., Petters J., Frech M., Seemann S., Thiel F.G., et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and protein misfolding in disorders of the liver and pancreas. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019;64:315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2019.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

