Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Properties of Propynoyl Betulin Derivatives against Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 38003677
- PMCID: PMC10671498
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216487
Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Properties of Propynoyl Betulin Derivatives against Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: In Vitro Studies
Abstract
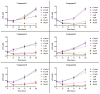
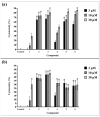
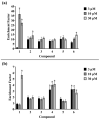
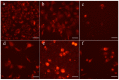
Due to the incidence of ovarian cancer (OC) and the limitations of available therapeutic strategies, it is necessary to search for novel therapeutic solutions. The aim of this study was to evaluate the cytotoxic effect of betulin 1 and its propynoyl derivatives 2-6 against ovarian cancer cells (SK-OV-3, OVCAR-3) and normal myofibroblasts (18Co). Paclitaxel was used as the reference compound. The propynoyl derivatives 2-6 exhibited stronger antiproliferative and cytotoxic activities compared to betulin 1. In both ovarian cancer cell lines, the most potent compound was 28-propynoylbetulin 2. In the case of compound 2, the calculated IC50 values were 0.2 µM for the SK-OV-3 cells and 0.19 µM for the OVCAR-3 cells. Under the same culture conditions, the calculated IC50 values for compound 6 were 0.26 µM and 0.59 µM, respectively. It was observed that cells treated with compounds 2 and 6 caused a decrease in the potential of the mitochondrial membrane and a significant change in cell morphology. Betulin 1, a diol from the group of pentacyclic triterpenes, has a confirmed wide spectrum of biological effects, including a significant anticancer effect. It is characterized by low bioavailability, which can be improved by introducing changes to its structure. The results showed that chemical modifications of betulin 1 only at position C-28 with the propynoyl group (compound 2) and additionally at position C-3 with the phosphate group (compound 3) or at C-29 with the phosphonate group (compound 6) allowed us to obtain compounds with greater cytotoxic activity than their parent compounds, which could be used to develop novel therapeutic systems effective in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: betulin derivatives; cytotoxicity; ovarian cancer; regulated cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Influence of betulin and 28-O-propynoylbetulin on proliferation and apoptosis of human melanoma cells (G-361).Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Feb 6;68:191-7. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1088757. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 24662787
-
Bacterial Biotransformation and Anticancer Activities of Betulin against A549, HepG2 and 5RP7 Cancer Cell Lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(12):1581-1593. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666201029102400. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33121415
-
The new esters derivatives of betulin and betulinic acid in epidermoid squamous carcinoma treatment - In vitro studies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 May;72:91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26054680
-
Betulinic Acid and its Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents.Med Res Rev. 2015 Nov;35(6):1127-55. doi: 10.1002/med.21353. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Med Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 26032847 Review.
-
Triphenylphosphonium Analogues of Betulin and Betulinic Acid with Biological Activity: A Comprehensive Review.J Nat Prod. 2019 Jun 28;82(6):1719-1730. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00830. Epub 2019 May 29. J Nat Prod. 2019. PMID: 31141361 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and preliminary cytotoxicity evaluation of water soluble pentacyclic triterpenoid phosphonates.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):28031. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76816-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39543237 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-Synthesis, Anti-Leukemia Activity, and Docking Study of Derivatives from 3α,24-Dihydroxylup-20(29)-en-28-Oic Acid.Molecules. 2025 Jul 30;30(15):3193. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153193. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807368 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Activity of Curcumin- and Resveratrol-Loaded Core-Shell Systems in Resistant and Sensitive Human Ovarian Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):41. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010041. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795900 Free PMC article.
-
Dammarane-Type 3,4-seco-Triterpenoid from Silver Birch (Betula pendula Roth) Buds Induces Melanoma Cell Death by Promotion of Apoptosis and Autophagy.Molecules. 2024 Aug 29;29(17):4091. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174091. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274939 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

