Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Jacobaea maritima and the Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities
- PMID: 38003704
- PMCID: PMC10671674
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216512
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Jacobaea maritima and the Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities
Abstract
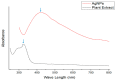
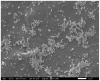
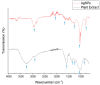
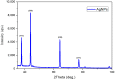
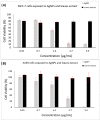
Much attention has been gained on green silver nanoparticles (green-AgNPs) in the medical field due to their remarkable effects against multi-drug resistant (MDR) microorganisms and targeted cancer treatment. In the current study, we demonstrated a simple and environment-friendly (i.e., green) AgNP synthesis utilizing Jacobaea maritima aqueous leaf extract. This leaf is well-known for its medicinal properties and acts as a reducing and stabilizing agent. Nanoparticle preparation with the desired size and shape was controlled by distinct parameters; for instance, temperature, extract concentration of salt, and pH. The characterization of biosynthesized AgNPs was performed by the UV-spectroscopy technique, dynamic light scattering, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier-transform infrared. The successful formation of AgNPs was confirmed by a surface plasmon resonance at 422 nm using UV-visible spectroscopy and color change observation with a particle size of 37± 10 nm and a zeta potential of -10.9 ± 2.3 mV. SEM further confirmed the spherical size and shape of AgNPs with a size varying from 28 to 52 nm. Antibacterial activity of the AgNPs was confirmed against all Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial reference and MDR strains that were used in different inhibitory rates, and the highest effect was on the E-coli reference strain (MIC = 25 μg/mL). The anticancer study of AgNPs exhibited an IC50 of 1.37 μg/mL and 1.98 μg/mL against MCF-7 (breast cancer cells) and A549 (lung cancer cells), respectively. Therefore, this green synthesis of AgNPs could have a potential clinical application, and further in vivo study is required to assess their safety and efficacy.
Keywords: Jacobaea maritima; antibacterial; anticancer; green synthesis; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pungle R., Nile S.H., Makwana N., Singh R., Singh R.P., Kharat A.S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Tridax procumbens Plant Extract and Screening of Its Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022;2022:9671594. doi: 10.1155/2022/9671594. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sibuyi N.R.S., Moabelo K.L., Meyer S., Skepu A., Onani M.O., Madiehe A.M., Meyer M. Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for Treatment of Obesity, Cancer and Anti-microbial Resistance: Highlights of the Department of Science and Innovation/Mintek Nanotechnology Innovation Centre Biolabels Research Node at the University of the Western Cape. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:10512. doi: 10.3390/app122010512. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

