Molecular Characteristics of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 38003734
- PMCID: PMC10671929
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216545
Molecular Characteristics of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
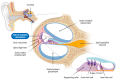
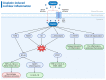
Cisplatin is a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent with proven efficacy in treating various malignancies, including testicular, ovarian, cervical, breast, bladder, head and neck, and lung cancer. Cisplatin is also used to treat tumors in children, such as neuroblastoma, osteosarcoma, and hepatoblastoma. However, its clinical use is limited by severe side effects, including ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, and retinal toxicity. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity manifests as irreversible, bilateral, high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in 40-60% of adults and in up to 60% of children. Hearing loss can lead to social isolation, depression, and cognitive decline in adults, and speech and language developmental delays in children. Cisplatin causes hair cell death by forming DNA adducts, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation, culminating in programmed cell death by apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, or ferroptosis. Contemporary medical interventions for cisplatin ototoxicity are limited to prosthetic devices, such as hearing aids, but these have significant limitations because the cochlea remains damaged. Recently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first therapy, sodium thiosulfate, to prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss in pediatric patients with localized, non-metastatic solid tumors. Other pharmacological treatments for cisplatin ototoxicity are in various stages of preclinical and clinical development. This narrative review aims to highlight the molecular mechanisms involved in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity, focusing on cochlear inflammation, and shed light on potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapeutic interventions to prevent or mitigate the ototoxic effects of cisplatin. We conducted a comprehensive literature search (Google Scholar, PubMed) focusing on publications in the last five years.
Keywords: cisplatin; cochlea; hearing loss; inflammation; ototoxicity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: From signaling network to therapeutic targets.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jan;157:114045. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114045. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36455457 Review.
-
Modulating the unfolded protein response with ISRIB mitigates cisplatin ototoxicity.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22382. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70561-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333235 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of the Grading Scales for the Detection of Ototoxicity in Children after Treatment of Neuroblastoma and Extracranial Germinal Tumor.Audiol Neurootol. 2023;28(1):32-42. doi: 10.1159/000526403. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Audiol Neurootol. 2023. PMID: 36191558
-
Prevalence and risk factors for cisplatin-induced hearing loss in children, adolescents, and young adults: a multi-institutional North American cohort study.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021 Apr;5(4):274-283. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00020-1. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 33581749 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular mechanisms and otoprotective strategies.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Jun;163:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33775853 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Compounds and Combinations Thereof against Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in a Rat Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 24;13(7):761. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070761. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061830 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel Matrix Containing Microcarriers for Dexamethasone Delivery to Protect Against Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss.Cureus. 2024 Oct 9;16(10):e71142. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71142. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39386930 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-based molecules in the treatment of cancer: From bench to bedside.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):759-779. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.057019. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis, oxidative stress and hearing loss: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(20):e38553. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38553. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39512327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Activity Increases Cisplatin Efficacy to Eliminate Metastatic Cells in Pediatric Liver Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 22;16(13):2300. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132300. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001363 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

