PYED-1 Overcomes Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 38003788
- PMCID: PMC10674209
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12111323
PYED-1 Overcomes Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
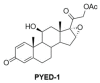
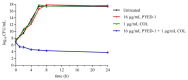
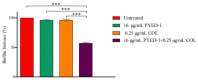
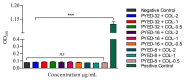
Antibiotic resistance has become more and more widespread over the recent decades, becoming a major global health problem and causing colistin to be increasingly used as an antibiotic of last resort. Acinetobacter baumannii, an opportunistic pathogen that has rapidly evolved into a superbug exhibiting multidrug-resistant phenotypes, is responsible for a large number of hospital infection outbreaks. With the intensive use of colistin, A. baumannii resistance to colistin has been found to increase significantly. In previous work, we identified a deflazacort derivative, PYED-1 (pregnadiene-11-hydroxy-16,17-epoxy-3,20-dione-1), which exhibits either direct-acting or synergistic activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative species and Candida spp., including A. baumannii. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antibacterial activity of PYED-1 in combination with colistin against both A. baumannii planktonic and sessile cells. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity of PYED-1 with and without colistin was assessed. Our results show that PYED-1 and colistin can act synergistically to produce a strong antimicrobial effect against multidrug-resistant populations of A. baumannii. Interestingly, our data reveal that PYED-1 is able to restore the efficacy of colistin against all colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates. This drug combination could achieve a much stronger antimicrobial effect than colistin while using a much smaller dosage of the drugs, additionally eliminating the toxicity and resistance issues associated with the use of colistin.
Keywords: antibiofilm molecules; antibiotic adjuvants; corticosteroids; killing kinetics; multidrug-resistant A. baumannii; synergistic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Colistin in Combination with Econazole against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Its Persisters.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0093722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00937-22. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35467374 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Pyrazole Compounds as Antibiotic Adjuvants Active against Colistin- and Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;11(12):1832. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11121832. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551489 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Activity of Colistin in Combination with Clofoctol against Colistin Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 21;11(2):e0427522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04275-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36802038 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Colistin Resistance, Virulence and Fitness in Acinetobacter baumannii.Antibiotics (Basel). 2017 Nov 21;6(4):28. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics6040028. Antibiotics (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29160808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches to overcome Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Exploring quorum quenching as a potential solution.Microb Pathog. 2023 Sep;182:106264. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106264. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Microb Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37474078 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Potential of N-Butyl-l-deoxynojirimycin (l-NBDNJ) in Models of Cystic Fibrosis as a Promising Antibacterial Agent.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 May 10;7(6):1807-1822. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00044. eCollection 2024 Jun 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38898954 Free PMC article.
-
Colistin Resistance Mechanism and Management Strategies of Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections.Pathogens. 2024 Nov 28;13(12):1049. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121049. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based targeting of the lipid A-modifying enzyme PmrC to contrast colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 28;15:1501051. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1501051. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39669780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics are Urgently Needed. [(accessed on 29 September 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

