Network-Based In Silico Analysis of New Combinations of Modern Drug Targets with Methotrexate for Response-Based Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 38003865
- PMCID: PMC10672378
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13111550
Network-Based In Silico Analysis of New Combinations of Modern Drug Targets with Methotrexate for Response-Based Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Methotrexate (MTX), sulfonamides, hydroxychloroquine, and leflunomide have consistently resulted in remission with relatively mild to moderate adverse effects in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Modern medications outperform traditional treatments in that they target the pathological processes that underlie the development of RA.
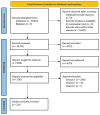
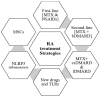
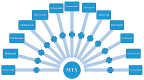
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, the authors accomplished a systematic review of the clinical efficacy of RA drugs, including the biologics such as Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha inhibitors (TNF-α i) like Etanercept, Infliximab, Golimumab, and Adalimumab, kinase inhibitors (JAK inhibitors including Baricitinib and Tofacitanib), SyK inhibitors like Fos-tamatinib, MAPK inhibitors such as Talmapimod, T-cell inhibitors (Abatacept), IL6 blockers (Tocilizumab), and B cells depleters (Rituximab). These drugs have been found to increase remission rates when combined with MTX. A bioinformatics-based network was designed applying STRING-MODEL and the DrugBank database for the aforementioned drugs and MTX and, finally, employed for this systematic review.
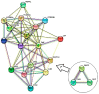
Results: Current research demonstrates that non-TNF-α inhibitor biologicals are particularly helpful in treating patients who did not respond well to conventional medications and TNF-α inhibitors. Despite being effective, these innovative drugs have a higher chance of producing hazardous side effects. The in silico investigations suggested an uncovered molecular interaction in combining MTX with other biological drugs. The STRING-MODEL showed that DHFR, TYMS, and ATIC, as the receptors of MTX, interact with each other but are not connected to the major interacted receptors.
Conclusions: New game-changing drugs including Mavrilimumab, Iguratimod, Upadacitinib, Fenebrutinib, and nanoparticles may be crucial in controlling symptoms in poorly managed RA patients. Emerging therapeutic targets like Toll-like 4 receptors, NLRP3 inflammasome complexes, and mesenchymal stem cells can further transform RA therapy.
Keywords: DMARDS; Inflammatory arthritis; JAK inhibitors; Rheumatoid arthritis; TLR4 receptor inhibition; new targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infection risk in patients undergoing treatment for inflammatory arthritis: non-biologics versus biologics.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Feb;16(2):207-228. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1705785. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31852268 Review.
-
Review of eight pharmacoeconomic studies of the value of biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Sep;12(7):555-69. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.7.555. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16981801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preliminary evaluation in rheumatoid arthritis activity in patients treated with TNF-alpha blocker plus methotrexate versus methotrexate or leflunomide alone.Rheumatol Int. 2007 May;27(7):641-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-006-0272-7. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Rheumatol Int. 2007. PMID: 17235556 Clinical Trial.
-
Real-world Effectiveness of Biologic Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis After Etanercept Discontinuation in the United Kingdom, France, and Germany.Clin Ther. 2017 Aug;39(8):1618-1627. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28729087
-
Baricitinib for Previously Treated Moderate or Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Jul;36(7):769-778. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0616-7. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29502174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and Regulatory Mechanisms of Comorbidity of Anxiety, Depression and ADHD: A GWAS Meta-Meta-Analysis Through the Lens of a System Biological and Pharmacogenomic Perspective in 18.5 M Subjects.J Pers Med. 2025 Mar 5;15(3):103. doi: 10.3390/jpm15030103. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40137419 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal Administration of Adalimumab-Loaded Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles: Effects on Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics.Small Sci. 2025 Jan 27;5(4):2400494. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400494. eCollection 2025 Apr. Small Sci. 2025. PMID: 40657186 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of mRNAs and miRNAs related to mitogen-activated kinases in HaCaT cell culture treated with lipopolysaccharide a and adalimumab.Cell Cycle. 2024 Feb;23(4):385-404. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2335051. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Cell Cycle. 2024. PMID: 38557266 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine self-administration attenuates brain glucose metabolism and functional connectivity in rats.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 6;20(6):e0324522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324522. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40478894 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

