Proteome Analysis of Bevacizumab Intervention in Experimental Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
- PMID: 38003895
- PMCID: PMC10672637
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13111580
Proteome Analysis of Bevacizumab Intervention in Experimental Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Abstract
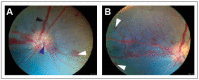
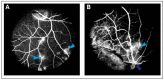
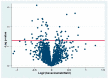
Bevacizumab is a frequently used inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the management of macular edema in central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO). Studying retinal protein changes in bevacizumab intervention may provide insights into mechanisms of action. In nine Danish Landrace pigs, experimental CRVO was induced in both eyes with argon laser. The right eyes received an intravitreal injection of 0.05 mL bevacizumab (n = 9), while the left control eyes received 0.05 mL saline water (NaCl). Retinal samples were collected 15 days after induced CRVO. Label-free quantification nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry identified 59 proteins that were regulated following bevacizumab treatment. Following bevacizumab intervention, altered levels of bevacizumab components, including the Ig gamma-1 chain C region and the Ig kappa chain C region, were observed. Changes in other significantly regulated proteins ranged between 0.58-1.73, including for the NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain (fold change = 1.73), protein-transport protein Sec24B (fold change = 1.71), glycerol kinase (fold change = 1.61), guanine-nucleotide-binding protein G(T) subunit-gamma-T1 (fold change = 0.67), and prefoldin subunit 6 (fold change = 0.58). A high retinal concentration of bevacizumab was achieved within 15 days. Changes in the additional proteins were limited, suggesting a narrow mechanism of action.
Keywords: bevacizumab; biomarker; mass spectrometry; proteome; proteomics; retina; retinal vein occlusion; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteome Analysis of Aflibercept Intervention in Experimental Central Retinal Vein Occlusion.Molecules. 2022 May 24;27(11):3360. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113360. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684299 Free PMC article.
-
Complement C3 is downregulated following ranibizumab intervention in experimental central retinal vein occlusion.Mol Vis. 2024 Jul 2;30:268-277. eCollection 2024. Mol Vis. 2024. PMID: 39563678 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal bevacizumab upregulates transthyretin in experimental branch retinal vein occlusion.Mol Vis. 2018 Nov 26;24:759-766. eCollection 2018. Mol Vis. 2018. PMID: 30581282 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 7;7(7):CD009510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32633861 Free PMC article.
-
Therapies for macular edema associated with central retinal vein occlusion: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.Ophthalmology. 2015 Apr;122(4):769-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.10.013. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Ophthalmology. 2015. PMID: 25576994 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

