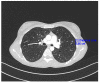
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex-A Case Study
- PMID: 38003913
- PMCID: PMC10672091
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13111598
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex-A Case Study
Abstract
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is characterized by lung cysts that cause lung deterioration, changes in the lymphatic system, and tumors in the kidneys. It mainly affects women of reproductive age and is a progressive disease. LAM can occur as an isolated disease or coexist with tuberous sclerosis (TSC). The source of LAM cells is unknown. Patients with confirmed LAM should be treated with an mTOR inhibitor, sirolimus, or everolimus. We present a case of LAM with TSC in a patient whose symptoms, including those in the lymph nodes and chyaloperitoneum, mainly concern the abdominal cavity.
Keywords: benign metastasizing leiomyomatosis; lymphangioleiomyomatosis; tuberous sclerosis complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Esposito A.J., Imani J., Shrestha S., Bagwe S., Lamattina A.M., Vivero M., Goldberg H.J., Rosas I.O., Henske E.P., El-Chemaly S.Y. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Circulating Levels of FGF23 and pulmonary diffusion. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2023;49:e20220356. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20220356. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ağaçkiran Y., Ertürk A., Yeşıller F.I., Hoca N.T., Ustün L.N., Capan N. Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A rare case. Turk. Patoloji Derg. 2014;30:233–236. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous