In Silico and In Vitro Exploration of Poziotinib and Olmutinib Synergy in Lung Cancer: Role of hsa-miR-7-5p in Regulating Apoptotic Pathway Marker Genes
- PMID: 38003971
- PMCID: PMC10673591
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59111923
In Silico and In Vitro Exploration of Poziotinib and Olmutinib Synergy in Lung Cancer: Role of hsa-miR-7-5p in Regulating Apoptotic Pathway Marker Genes
Abstract
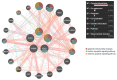
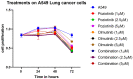
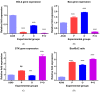
Background and objectives: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is often caused by EGFR mutations, leading to overactive cell growth pathways. Drug resistance is a significant challenge in lung cancer treatment, affecting therapy effectiveness and patient survival. However, combining drugs in research shows promise in addressing or delaying resistance, offering a more effective approach to cancer treatment. In this study, we investigated the potential alterations in the apoptotic pathway in A549 cells induced by a combined targeted therapy using tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) olmutinib and poziotinib, focusing on cell proliferation, differential gene expression, and in silico analysis of apoptotic markers. Methods: A combined targeted therapy involving olmutinib and poziotinib was investigated for its impact on the apoptotic pathway in A549 cells. Cell proliferation, quantitative differential gene expression, and in silico analysis of apoptotic markers were examined. A549 cells were treated with varying concentrations (1, 2.5, and 5 μM) of poziotinib, olmutinib, and their combination. Results: Treatment with poziotinib, olmutinib, and their combination significantly reduced cell proliferation, with the most pronounced effect at 2.5 μM (p < 0.005). A synergistic antiproliferative effect was observed with the combination of poziotinib and olmutinib (p < 0.0005). Quantitative differential gene expression showed synergistic action of the drug combination, impacting key apoptotic genes including STK-11, Bcl-2, Bax, and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. In silico analysis revealed direct interactions between EGFR and ERBB2 genes, accounting for 77.64% of their interactions, and 8% co-expression with downstream apoptotic genes. Molecular docking indicated strong binding of poziotinib and olmutinib to extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathway markers, with binding energies of -9.4 kcal/mol and -8.5 kcal/mol, respectively, on interacting with STK-11. Conclusions: Combining poziotinib and olmutinib therapies may significantly improve drug tolerance and conquer drug resistance more effectively than using them individually in lung cancer patients, as suggested by this study's mechanisms.
Keywords: Bax; Bcl-2; STK-11; lung cancer; olmutinib; poziotinib; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic landscape of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR T790M-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer. 2020 Jun 1;126(11):2704-2712. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32809. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32154925
-
Safety, tolerability, and anti-tumor activity of olmutinib in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutation: A single arm, open label, phase 1/2 trial.Lung Cancer. 2019 Sep;135:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31447004 Clinical Trial.
-
Olmutinib in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer after failure of first-line epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy: A global, phase 2 study.Cancer. 2021 May 1;127(9):1407-1416. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33385. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33434335 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanisms and management of 3rd‑generation EGFR‑TKI resistance in advanced non‑small cell lung cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Nov;59(5):90. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5270. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34558640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Derivative CU4c Exhibits HDAC-Inhibitory and Anticancer Activities Against Human Lung Cancer Cells In Vitro and in Mouse Xenograft Models.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;18(7):960. doi: 10.3390/ph18070960. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732250 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the anti-breast cancer activity potential of east Kalimantan propolis by In vitro and bioinformatics analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33636. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33636. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071605 Free PMC article.
-
Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Apr 16;60(4):639. doi: 10.3390/medicina60040639. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38674285 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

