A De Novo Frameshift Mutation in RPL5 with Classical Phenotype Abnormalities and Worsening Anemia Diagnosed in a Young Adult-A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 38004002
- PMCID: PMC10673431
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59111953
A De Novo Frameshift Mutation in RPL5 with Classical Phenotype Abnormalities and Worsening Anemia Diagnosed in a Young Adult-A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
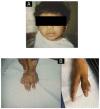
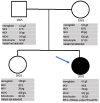
Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA) is a congenital bone marrow failure syndrome associated with malformations. DBA is related to defective ribosome biogenesis, which impairs erythropoiesis, causing hyporegenerative macrocytic anemia. The disease has an autosomal dominant inheritance and is commonly diagnosed in the first year of life, requiring continuous treatment. We present the case of a young woman who, at the age of 21, developed severe symptomatic anemia. Although, due to malformations, a congenital syndrome had been suspected since birth, a confirmation diagnosis was not made until the patient was referred to our center for an evaluation of her anemia. In her neonatal medical history, she presented with anemia that required red blood cell transfusions, but afterwards remained with a stable, mild, asymptomatic anemia throughout her childhood and adolescence. Her family history was otherwise unremarkable. To explain the symptomatic anemia, vitamin deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, bleeding causes, and myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms were investigated and ruled out. A molecular investigation showed the RPL5 gene variant c.392dup, p.(Asn131Lysfs*6), confirming the diagnosis of DBA. All family members have normal blood values and none harbored the mutation. Here, we will discuss the unusual evolution of this case and revisit the literature.
Keywords: Diamond–Blackfan anemia; RPL5; bone marrow failure; eltrombopag; erythroaplasia; pure red cell aplasia; ribosomopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D. has no competing interests. N.P. has no competing interests. M.Di. has no competing interests. A.R. has received research funding from Novartis, CSL Behring, and AG Alexion, has received honoraria from AG Alexion and Novartis, has received honoraria for advisory board meetings from AG Alexion, BMS, Novartis, OrPhaSwiss GmbH, and Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AG.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diamond-Blackfan anemia: genotype-phenotype correlations in Italian patients with RPL5 and RPL11 mutations.Haematologica. 2010 Feb;95(2):206-13. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.011783. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 19773262 Free PMC article.
-
Diamond-Blackfan anemia with mandibulofacial dystostosis is heterogeneous, including the novel DBA genes TSR2 and RPS28.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Sep;164A(9):2240-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36633. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24942156 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical phenotype and genetic analysis of RPS19, RPL5, and RPL11 genes in Greek patients with Diamond Blackfan Anemia.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014 Dec;61(12):2249-55. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25183. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25132370
-
Untangling the phenotypic heterogeneity of Diamond Blackfan anemia.Semin Hematol. 2011 Apr;48(2):124-35. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2011.02.003. Semin Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21435509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis in Diamond-Blackfan anemia.Int J Hematol. 2010 Oct;92(3):413-8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-010-0693-7. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Int J Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20882441 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Diamond-Blackfan anemia in adulthood: case series and review of the literature.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03490-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 39702189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Willig T.-N., Niemeyer C.M., Leblanc T., Tiemann C., Robert A., Budde J., Lambiliotte A., Kohne E., Souillet G., Eber S., et al. Identification of new prognosis factors from the clinical and epidemiologic analysis of a registry of 229 Diamond-Blackfan anemia patients. Pediatr. Res. 1999;46:553. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199911000-00011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sieff C. Diamond-Blackfan Anemia. GeneReviews®. [(accessed on 30 August 2023)]; Published 25 June 2009. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7047/
-
- Vlachos A., Ball S., Dahl N., Alter B.P., Sheth S., Ramenghi U., Meerpohl J., Karlsson S., Liu J.M., Leblanc T., et al. Diagnosing and treating Diamond Blackfan anaemia: Results of an international clinical consensus conference. Br. J. Haematol. 2008;142:859–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07269.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

