Microbiota-Accessible Boron-Containing Compounds in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- PMID: 38004014
- PMCID: PMC10673453
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59111965
Microbiota-Accessible Boron-Containing Compounds in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Abstract
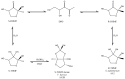
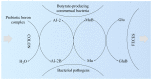
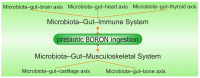
The microbiota-gut-brain axis has garnered increasing attention in recent years for its role in various health conditions, including neuroinflammatory disorders like complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). CRPS is a debilitating condition characterized by chronic neuropathic pain, and its etiology and pathophysiology remain elusive. Emerging research suggests that alterations in the gut microbiota composition and function could play a significant role in CRPS development and progression. Our paper explores the implications of microbiota in CRPS and the potential therapeutic role of boron (B). Studies have demonstrated that individuals with CRPS often exhibit dysbiosis, with imbalances in beneficial and pathogenic gut bacteria. Dysbiosis can lead to increased gut permeability and systemic inflammation, contributing to the chronic pain experienced in CRPS. B, an essential trace element, has shown promise in modulating the gut microbiome positively and exerting anti-inflammatory effects. Recent preclinical and clinical studies suggest that B supplementation may alleviate neuropathic pain and improve CRPS symptoms by restoring microbiota balance and reducing inflammation. Our review highlights the complex interplay between microbiota, inflammation, and neuropathic pain in CRPS and underscores the potential of B as a novel therapeutic approach to target the microbiota-gut-brain axis, offering hope for improved management of this challenging condition.
Keywords: boron-containing compounds; complex regional pain syndrome; gut–brain axis; gut–immune system axis; gut–musculoskeletal axis; microbiota; prebiotic boron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Mekhail N., Deer T.R., Poree L., Staats P.S., Burton A.W., Connolly A.T., Karst E., Mehanny D.S., Saweris Y., Levy R.M. Cost-effectiveness of dorsal root ganglion stimulation or spinal cord stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome. Neuromodulation. 2021;24:708–718. doi: 10.1111/ner.13134. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

