The Role of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 38004032
- PMCID: PMC10672798
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59111984
The Role of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
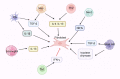
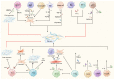
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating disease of unknown etiology with limited treatment options. The role of the immune system in IPF has received increasing attention. Uncontrolled immune responses drive the onset and progression of IPF. This article provides an overview of the role of innate immune cells (including macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, dendritic cells, nature killer cells, nature kill cells and γδ T cells) and adaptive immune cells (including Th1 cells, Th2 cells, Th9 cells, Th17 cells, Th22 cells, cytotoxic T cells, B lymphocytes and Treg cells) in IPF. In addition, we review the current status of pharmacological treatments for IPF and new developments in immunotherapy. A deeper comprehension of the immune system's function in IPF may contribute to the development of targeted immunomodulatory therapies that can alter the course of the disease.
Keywords: T cells; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; immune cell; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peripheral depletion of NK cells and imbalance of the Treg/Th17 axis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients.Cytokine. 2014 Apr;66(2):119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.12.003. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24418172
-
Regulatory Immune Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Friends or Foes?Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 22;12:663203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663203. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic Cells Are the Intriguing Players in the Puzzle of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 30;12:664109. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.664109. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment.Respir Med. 2019 Feb;147:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.12.015. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30704705 Review.
-
Deleterious Role of Th9 Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Cells. 2021 Nov 17;10(11):3209. doi: 10.3390/cells10113209. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831433 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Co-Mn Complex Oxide Nanoparticles as Potential Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Agents for Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment.Molecules. 2024 Oct 29;29(21):5106. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215106. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519747 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Analysis of Key Immune- and Inflammation-Related Genes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 11;18:1993-2009. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S489210. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39959639 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Qingre Sanjie Jiaonang on Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Pilot Study.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 31;18:4551-4565. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S479432. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40191096 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Differential Expression of Non-coding RNAs (TP53TG1, LINC00342, MALAT1, DNM3OS, miR-126-3p, miR-200a-3p, miR-18a-5p) and Protein-Coding Genes (PTEN, FOXO3) and Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jan 29. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-11012-z. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39881079
-
A Simple Ratio in a Complex Disease: Exploring the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 18;14(14):5100. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145100. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raghu G., Remy-Jardin M., Richeldi L., Thomson C.C., Inoue Y., Johkoh T., Kreuter M., Lynch D.A., Maher T.M., Martinez F.J., et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022;205:e18–e47. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202202-0399ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

