How to Choose the Right Treatment for Membranous Nephropathy
- PMID: 38004046
- PMCID: PMC10673286
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59111997
How to Choose the Right Treatment for Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
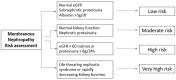
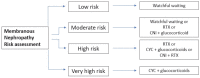
Membranous nephropathy is an autoimmune disease affecting the glomeruli and is one of the most common causes of nephrotic syndrome. In the absence of any therapy, 35% of patients develop end-stage renal disease. The discovery of autoantibodies such as phospholipase A2 receptor 1, antithrombospondin and neural epidermal growth factor-like 1 protein has greatly helped us to understand the pathogenesis and enable the diagnosis of this disease and to guide its treatment. Depending on the complications of nephrotic syndrome, patients with this disease receive supportive treatment with diuretics, ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, lipid-lowering agents and anticoagulants. After assessing the risk of progression of end-stage renal disease, patients receive immunosuppressive therapy with various drugs such as cyclophosphamide, steroids, calcineurin inhibitors or rituximab. Since immunosuppressive drugs can cause life-threatening side effects and up to 30% of patients do not respond to therapy, new therapeutic approaches with drugs such as adrenocorticotropic hormone, belimumab, anti-plasma cell antibodies or complement-guided drugs are currently being tested. However, special attention needs to be paid to the choice of therapy in secondary forms or in specific clinical contexts such as membranous disease in children, pregnant women and patients undergoing kidney transplantation.
Keywords: belimumab; bortezomib; complement children; glomerulonephritis; immunosuppressive therapy; membranous nephropathy; nephrotic syndrome; pregnancy; renal transplant; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Membranous Nephropathy: Updates on Management.Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024 Jul;31(4):299-308. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2024.04.004. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024. PMID: 39084755 Review.
-
[Membranous nephropathy: New insights in therapeutic approach].Nephrol Ther. 2017 Apr;13 Suppl 1:S83-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2017.02.002. Nephrol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28577748 French.
-
[Membranous nephropathy: Pathophysiology and natural history].Nephrol Ther. 2017 Apr;13 Suppl 1:S75-S81. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2017.01.012. Nephrol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28577747 Review. French.
-
Idiopathic membranous nephropathy in children treated with rituximab: report of two cases.Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Jun;33(6):1089-1092. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-3923-5. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29546599
-
Primary membranous nephropathy: an endless story.J Nephrol. 2023 Mar;36(2):563-574. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01461-3. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36251213 Review.
Cited by
-
Overlap of Scleroderma and Class V Lupus Nephritis: A Rare Autoimmune Confluence.Cureus. 2024 Mar 26;16(3):e56990. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56990. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38681456 Free PMC article.
-
Membranous nephropathy: pathogenesis and treatments.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jun 29;5(7):e614. doi: 10.1002/mco2.614. eCollection 2024 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38948114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of progress on complement and primary membranous nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e38990. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038990. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39029058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

