In Vitro Assessment of Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seeds Extract on 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Raw264.7 Macrophages
- PMID: 38004077
- PMCID: PMC10673321
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59112028
In Vitro Assessment of Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seeds Extract on 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Raw264.7 Macrophages
Abstract
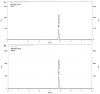
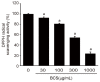
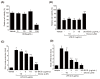
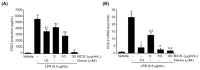
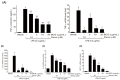
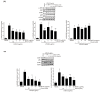
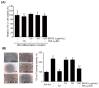
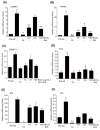
Background and Objectives: This study evaluated the in vitro anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seed extract (BCS extract) as a potential candidate for developing herbal formulations targeting metabolic disorders. Materials and Methods: We evaluated the BCS extract by assessing its 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrohydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity, levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nitric oxide (NO), and mRNA expression levels of key pro-inflammatory mediators. We also quantified the phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling molecules. To assess anti-adipogenic effects, we used differentiated 3T3-L1 cells and BCS extract in doses from 10 to 100 μg/mL. We also determined mRNA levels of key adipogenic genes, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/BEPα), adipocyte protein 2 (aP2), lipoprotein lipase (LPL), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and sterol-regulated element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Results: This study showed a concentration-dependent DPPH radical scavenging activity and no toxicity at concentrations up to 30 μg/mL in Raw264.7 cells. BCS extract showed an IC50 of 328.77 ± 20.52 μg/mL. Notably, pre-treatment with BCS extract (30 μg/mL) significantly enhanced cell viability in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated Raw264.7 cells. BCS extract treatment effectively inhibited LPS-induced production of PGE2 and NO, as well as the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible NO synthase (iNOS), interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, possibly by limiting the phosphorylation of p38, p65, inhibitory κBα (I-κBα), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). It also significantly attenuated lipid accumulation and key adipogenic genes in 3T3-L1 cells. Conclusions: This study highlights the in vitro anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory potential of BCS extract, underscoring its potential as a promising candidate for managing metabolic disorders.
Keywords: 3T3-L1 cells; Raw264.7 cells; adipogenic differentiation; oil red O; pro-inflammatory mediators.
Conflict of interest statement
J.-K.K. and Y.-S.C. are employed at AriBnC Ltd., and in this research, they only contributed to the preparation and analysis of raw materials to a limited extent. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-oxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Ethanol Extract from Polygala sibirica L. var megalopha Fr. on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Oct;29(10):905-913. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3602-7. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37434032
-
Ethyl acetate fraction from Nymphaea hybrida Peck modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and acute inflammation murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113698. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113698. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33338590
-
Saikosaponin A and D Inhibit Adipogenesis via the AMPK and MAPK Signaling Pathways in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 22;22(21):11409. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111409. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768840 Free PMC article.
-
Dermaceutical Utilization of Nigella sativa Seeds: Applications and Opportunities.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2024 Jan;74(1):5-17. doi: 10.1055/a-2196-1815. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2024. PMID: 38016656 Review.
-
An Overview of Conventional and Black Cumin Seeds (Nigella sativa) Therapy in the Management of Nipah Viral Infection.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(2):e251023222677. doi: 10.2174/0118715265258029231017112421. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37885111 Review.
Cited by
-
Nigella sativa: A Comprehensive Review of Its Therapeutic Potential, Pharmacological Properties, and Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13410. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413410. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kunitomi M., Wada J., Takahashi K., Tsuchiyama Y., Mimura Y., Hida K., Miyatake N., Fujii M., Kira S., Shikata K., et al. Relationship between reduced serum IGF-I levels and accumulation of visceral fat in Japanese men. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002;26:361–369. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801899. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hida K., Wada J., Eguchi J., Zhang H., Baba M., Seida A., Hashimoto I., Okada T., Yasuhara A., Nakatsuka A., et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: A unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:10610–10615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504703102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

