Examining the Role of Vitamin D in Caries Susceptibility in Children's Deciduous Teeth: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38004220
- PMCID: PMC10675460
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15224826
Examining the Role of Vitamin D in Caries Susceptibility in Children's Deciduous Teeth: A Systematic Review
Abstract
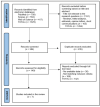
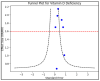
The global prevalence of dental caries in deciduous teeth remains a significant health concern, affecting almost 70% of children by the age of six in specific regions. This systematic review aspired to methodically investigate the association between vitamin D levels and susceptibility to caries in children's deciduous teeth. A detailed search, guided by the PRISMA and PROSPERO guidelines, was conducted across three prominent electronic databases: PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus, culminating in August 2023. The search integrated various keywords related to vitamin D and dental caries in primary dentition, yielding an initial pool of 1678 articles. After meticulous scrutiny, seven studies with a total of 7655 participants were deemed suitable for inclusion. The studies represented diverse geographical regions, showcasing varied vitamin D levels and sun exposure. Patient habits like brushing frequency, dental visits, and vitamin consumption also varied across studies. The analysis pinpointed vitamin D deficiency as a potential risk factor in some of the studies, with Odds Ratios (OR) ranging from 0.68 to 2.15. Statistically significant associations between vitamin D deficiency and caries susceptibility were documented in three studies (ORs of 2.15, 1.98, and 1.70). This comprehensive review elucidates the complex relationship between vitamin D levels and dental caries in children's deciduous teeth. While some studies spotlight vitamin D's pivotal role in dental health, inconsistencies across studies and regional differences necessitate more in-depth, globally representative investigations. Ensuring optimal vitamin D levels may play an integral role in dental health strategies. However, it is important to highlight that the roles of these studied factors might differ in deciduous teeth compared to permanent teeth.
Keywords: dental caries; dentistry; food supplements; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
WITHDRAWN: Dental fillings for the treatment of caries in the primary dentition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 17;10(10):CD004483. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004483.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27748505 Free PMC article.
-
Dental fillings for the treatment of caries in the primary dentition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;(2):CD004483. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004483.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 17;10:CD004483. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004483.pub3. PMID: 19370602 Updated.
-
Sealants for preventing dental caries in primary teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 11;2(2):CD012981. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012981.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35146744 Free PMC article.
-
Atraumatic restorative treatment versus conventional restorative treatment for managing dental caries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 28;12(12):CD008072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008072.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29284075 Free PMC article.
-
Direct composite resin fillings versus amalgam fillings for permanent posterior teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 13;8(8):CD005620. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005620.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34387873 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Strategies to build stronger bones in Indian children: Challenges for implementation.Indian J Med Res. 2024 Mar & Apr;159(3 & 4):315-321. doi: 10.25259/IJMR_233_2024. Indian J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39361795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Systemic Role of Diet in Dental Caries Development and Arrest: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 May 13;16(10):1463. doi: 10.3390/nu16101463. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38794700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between Maternal Prenatal Vitamin D Status and Early Childhood Caries in Their Children: A Cross-sectional Survey.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Aug;17(8):860-863. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2836. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39372353 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical