Dietary and Nutritional Interventions in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Pediatrics
- PMID: 38004223
- PMCID: PMC10674812
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15224829
Dietary and Nutritional Interventions in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Pediatrics
Abstract
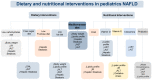
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is pediatrics' most common chronic liver disease. The incidence is high in children and adolescents with obesity, which is associated with an increased risk of disease progression. Currently, there is no effective drug therapy in pediatrics; therefore, lifestyle interventions remain the first line of treatment. This review aims to present an updated compilation of the scientific evidence for treating this pathology, including lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and dietary changes, highlighting specific nutritional strategies. The bibliographic review was carried out in different databases, including studies within the pediatric population where dietary and/or nutritional interventions were used to treat NAFLD. Main interventions include diets low in carbohydrates, free sugars, fructose, and lipids, in addition to healthy eating patterns and possible nutritional interventions with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA and DHA), amino acids (cysteine, L-carnitine), cysteamine, vitamins, and probiotics (one strain or multi-strain). Lifestyle changes remain the main recommendation for children with NAFLD. Nevertheless, more studies are required to elucidate the effectiveness of specific nutrients and bioactive compounds in this population.
Keywords: eating patterns; exercise; pediatric NAFLD; polyunsaturated fatty acids; vitamins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Trandafir L.M., Frasinariu O.E., Leon-Constantin M.M., Chiriac Ş., Trandafirescu M.F., Miron I.C., Luca A.C., Iordache A.C., Cojocaru E. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—A changing diagnostic paradigm. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020;61:1023–1031. doi: 10.47162/RJME.61.4.04. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li J., Ha A., Rui F., Zou B., Yang H., Xue Q., Hu X., Xu Y., Henry L., Barakat M., et al. Meta-analysis: Global prevalence, trend and forecasting of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents, 2000–2021. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022;56:396–406. doi: 10.1111/apt.17096. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

