Carborane-Based ABCG2-Inhibitors Sensitize ABC-(Over)Expressing Cancer Cell Lines for Doxorubicin and Cisplatin
- PMID: 38004447
- PMCID: PMC10674596
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111582
Carborane-Based ABCG2-Inhibitors Sensitize ABC-(Over)Expressing Cancer Cell Lines for Doxorubicin and Cisplatin
Abstract
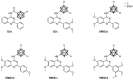
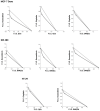
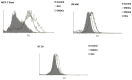
The ABCG2 transporter protein, as part of several known mechanisms involved in multidrug resistance, has the ability to transport a broad spectrum of substrates out of the cell and is, therefore, considered as a potential target to improve cancer therapies or as an approach to combat drug resistance in cancer. We have previously reported carborane-functionalized quinazoline derivatives as potent inhibitors of human ABCG2 which effectively reversed breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-mediated mitoxantrone resistance. In this work, we present the evaluation of our most promising carboranyl BCRP inhibitors regarding their toxicity towards ABCG2-expressing cancer cell lines (MCF-7, doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7 or MCF-7 Doxo, HT29, and SW480) and, consequently, with the co-administration of an inhibitor and therapeutic agent, their ability to increase the efficacy of therapeutics with the successful inhibition of ABCG2. The results obtained revealed synergistic effects of several inhibitors in combination with doxorubicin or cisplatin. Compounds DMQCa, DMQCc, and DMQCd showed a decrease in IC50 value in ABCB1- and ABCG2-expressing SW480 cells, suggesting a possible targeting of both transporters. In an HT29 cell line, with the highest expression of ABCG2 among the tested cell lines, using co-treatment of doxorubicin and DMQCd, the effective inhibitory concentration of the antineoplastic agent could be reduced by half. Interestingly, co-treatment of compound QCe with cisplatin, which is not an ABCG2 substrate, showed synergistic effects in MCF-7 Doxo and HT29 cells (IC50 values halved or reduced by 20%, respectively). However, a literature-known upregulation of cisplatin-effluxing ABC transporters and their effective inhibition by the carborane derivatives emerges as a possible reason.
Keywords: ABCG2; breast cancer resistance protein; carborane; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carboranes as Potent Phenyl Mimetics: A Comparative Study on the Reversal of ABCG2-Mediated Drug Resistance by Carboranylquinazolines and Their Organic Isosteres.ChemMedChem. 2024 Jan 15;19(2):e202300506. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300506. Epub 2023 Dec 11. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 38012078
-
The More the Better-Investigation of Polymethoxylated N-Carboranyl Quinazolines as Novel Hybrid Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitors.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 10;15(1):241. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010241. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678870 Free PMC article.
-
2-Carboranylquinazoline: The Path to an ABCG2 Inhibitor.ChemMedChem. 2023 Jun 1;18(11):e202300094. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300094. Epub 2023 Apr 14. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 36988057
-
Multidrug resistance mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2).Oncogene. 2003 Oct 20;22(47):7340-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206938. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14576842 Review.
-
Human ABC transporter ABCG2/BCRP expression in chemoresistance: basic and clinical perspectives for molecular cancer therapeutics.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2014 Feb 5;7:53-64. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S38295. eCollection 2014. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2014. PMID: 24523596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

