Analgesic Activity of 5-Acetamido-2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid Derivatives and an In-Vivo and In-Silico Analysis of Their Target Interactions
- PMID: 38004449
- PMCID: PMC10674373
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111584
Analgesic Activity of 5-Acetamido-2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid Derivatives and an In-Vivo and In-Silico Analysis of Their Target Interactions
Abstract
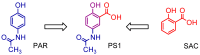
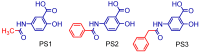
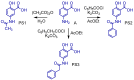
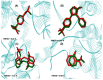
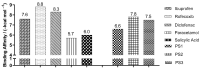
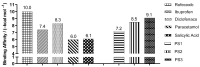
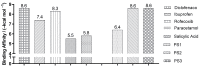
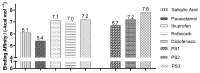
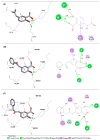
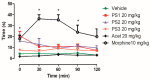
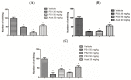
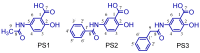
The design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with better activity and lower side effects are big challenges today. In this work, two 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid derivatives were proposed, increasing the alkyl position (methyl) in an acetamide moiety, and synthesized, and their structural elucidation was performed using 1H NMR and 13C NMR. The changes in methyl in larger groups such as phenyl and benzyl aim to increase their selectivity over cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). These 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid derivatives were prepared using classic methods of acylation reactions with anhydride or acyl chloride. Pharmacokinetics and toxicological properties were predicted using computational tools, and their binding affinity (kcal/mol) with COX-2 receptors (Mus musculus and Homo sapiens) was analyzed using docking studies (PDB ID 4PH9, 5KIR, 1PXX and 5F1A). An in-silico study showed that 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid derivates have a better bioavailability and binding affinity with the COX-2 receptor, and in-vivo anti-nociceptive activity was investigated by means of a writhing test induced by acetic acid and a hot plate. PS3, at doses of 20 and 50 mg/kg, reduced painful activity by 74% and 75%, respectively, when compared to the control group (20 mg/kg). Regarding the anti-nociceptive activity, the benzyl showed reductions in painful activity when compared to acetaminophen and 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid. However, the proposed derivatives are potentially more active than 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid and they support the design of novel and safer derivative candidates. Consequently, more studies need to be conducted to evaluate the different pharmacological actions, the toxicity of possible metabolites that can be generated, and their potential use in inflammation and pain therapy.
Keywords: 5-acetamido-2-hydroxy benzoic acid; ADME; analgesic; molecular docking; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of analgesic and antiplatelet activity of 2-((3-(chloromethyl)benzoyl)oxy)benzoic acid.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019 Dec;145:106364. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.106364. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019. PMID: 31356853
-
Design, synthesis, biological and computational screening of novel pyridine-based thiadiazole derivatives as prospective anti-inflammatory agents.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 9;10(8):e29390. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29390. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38655368 Free PMC article.
-
Oil from the fruits of Pterodon emarginatus Vog.: A traditional anti-inflammatory. Study combining in vivo and in silico.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Aug 10;222:107-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.041. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29723629
-
Synthesis and anti-nociceptive potential of isoxazole carboxamide derivatives.BMC Chem. 2019 Jan 29;13(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13065-019-0518-6. eCollection 2019 Dec. BMC Chem. 2019. PMID: 31355366 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of novel 4-fluorobenzamide-based derivatives as promising anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents with an enhanced gastric tolerability and COX-inhibitory activity.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Oct;115:105253. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105253. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34390973
References
-
- Richy F., Bruyere O., Ethgen O., Rabenda V., Bouvenot G., Audran M., Herrero-Beaumont G., Moore A., Eliakim R., Haim M., et al. Time dependent risk of gastrointestinal complications induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use: A consensus statement using a meta-analytic approach. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004;63:759–766. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.015925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borges R.S. Planejamento, Síntese e Avaliação Antioxidante de Inibidores Fenólicos da PGES Derivados da Associação p-Aminofenol e Salicilatos. Tese de Doutorado em Neurociências e Biologia Celular, UFPA; Belém, Brazil: 2007.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

