A Pharmacovigilance Study Regarding the Risk of Antibiotic-Associated Clostridioides difficile Infection Based on Reports from the EudraVigilance Database: Analysis of Some of the Most Used Antibiotics in Intensive Care Units
- PMID: 38004450
- PMCID: PMC10675398
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111585
A Pharmacovigilance Study Regarding the Risk of Antibiotic-Associated Clostridioides difficile Infection Based on Reports from the EudraVigilance Database: Analysis of Some of the Most Used Antibiotics in Intensive Care Units
Abstract
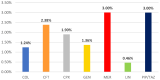
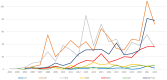
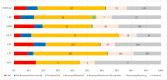
The Gram-positive anaerobic bacterium Clostridioides difficile (CD) can produce intense exotoxins, contributing to nosocomial infections, and it is the most common cause of health-care-associated infectious diarrhea. Based on spontaneous Individual Case Safety Reports from EudraVigilance (EV), we conducted a descriptive analysis of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) cases that reported a spontaneous adverse reaction related to using ceftriaxone, colistimethate, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, linezolid, meropenem, and piperacillin/tazobactam. Most ADR reports registered in EV that were related to CDI were associated with ceftriaxone (33%), ciprofloxacin (28%), and piperacillin/tazobactam (21%). Additionally, the disproportionality analysis performed showed that all studied antibiotics had a lower reporting probability when compared to clindamycin. A causal relationship between a drug and the occurrence of an adverse reaction cannot be established from EV data alone because the phenomena of underreporting, overreporting, and reporting bias may affect the results. Based on the analysis of the collected data, this study underlines the importance of surveillance and monitoring programs for the consumption of antibiotics. Furthermore, it is essential to use standardized laboratory tests to define CDI's nature accurately. To prevent this infection, specialists should collaborate and adhere strictly to antibiotic stewardship programs, hygiene practices, and isolation protocols.
Keywords: Clostridioides difficile infection; EudraVigilance; antibiotic; descriptive analysis; disproportionality analysis; pharmacovigilance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Real-World Study on the Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Relationship between Antibiotic Exposure and Clostridioides difficile Infection.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;13(2):144. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13020144. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391530 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse Drug Reactions Relevant to Drug Resistance and Ineffectiveness Associated with Meropenem, Linezolid, and Colistin: An Analysis Based on Spontaneous Reports from the European Pharmacovigilance Database.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 May 16;12(5):918. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050918. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237821 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of patients infected with Clostridioides difficile at a Saudi Tertiary Academic Medical Center and assessment of antibiotic duration.Gut Pathog. 2021 Feb 17;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13099-021-00405-9. Gut Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33593421 Free PMC article.
-
Clostridioides difficile resistance to antibiotics, including post-COVID-19 data.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Jul-Dec;16(10):925-938. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2023.2252331. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37642560 Review.
-
Burden of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) - a systematic review of the epidemiology of primary and recurrent CDI.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 19;21(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06147-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34016040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uncommon Septic Arthritis of the Hip Joint in an Immunocompetent Adult Patient Due to Bacillus pumilus and Paenibacillus barengoltzii Managed with Long-Term Treatment with Linezolid: A Case Report and Short Literature Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 18;16(12):1743. doi: 10.3390/ph16121743. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139869 Free PMC article.
-
An Assessment of Semaglutide Safety Based on Real World Data: From Popularity to Spontaneous Reporting in EudraVigilance Database.Biomedicines. 2024 May 18;12(5):1124. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051124. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791086 Free PMC article.
-
TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm-Opportunities and Challenges.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 28;12(4):684. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040684. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Diagnosis and Management of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Systematic Evaluation of Biofilm Detection Methods and Bacterial Colonization on Endotracheal Tubes.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 28;12(10):1966. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12101966. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance of ESKAPE Group Bacteria Isolated from Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit of a County Emergency Hospital in Romania.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;13(5):400. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050400. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birlutiu V., Mircea Birlutiu R., Rusu H.M. The Influence of the Use of Metronidazole Associated with Vancomycin in Reducing the Mortality Rate at 30 Days in Patients with Clostridium difficile Infection. Biomed. Res. 2018;29:606–609. doi: 10.4066/biomedicalresearch.29-17-346. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

