Neuroprotective Effects of Davallia mariesii Roots and Its Active Constituents on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in In Vivo and In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 38004471
- PMCID: PMC10675602
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111606
Neuroprotective Effects of Davallia mariesii Roots and Its Active Constituents on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in In Vivo and In Vitro Studies
Abstract
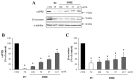
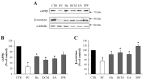
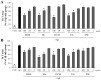
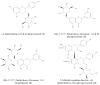
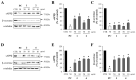
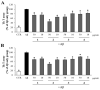
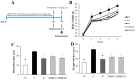
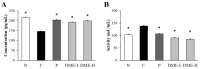
Beta-amyloid (Aβ) proteins, major contributors to Alzheimer's disease (AD), are overproduced and accumulate as oligomers and fibrils. These protein accumulations lead to significant changes in neuronal structure and function, ultimately resulting in the neuronal cell death observed in AD. Consequently, substances that can inhibit Aβ production and/or accumulation are of great interest for AD prevention and treatment. In the course of an ongoing search for natural products, the roots of Davallia mariesii T. Moore ex Baker were selected as a promising candidate with anti-amyloidogenic effects. The ethanol extract of D. mariesii roots, along with its active constituents, not only markedly reduced Aβ production by decreasing β-secretase expression in APP-CHO cells (Chinese hamster ovary cells which stably express amyloid precursor proteins), but also exhibited the ability to diminish Aβ aggregation while enhancing the disaggregation of Aβ aggregates, as determined through the Thioflavin T (Th T) assay. Furthermore, in an in vivo study, the extract of D. mariesii roots showed potential (a tendency) for mitigating scopolamine-induced memory impairment, as evidenced by results from the Morris water maze test and the passive avoidance test, which correlated with reduced Aβ deposition. Additionally, the levels of acetylcholine were significantly elevated, and acetylcholinesterase levels significantly decreased in the brains of mice (whole brains). The treatment with the extract of D. mariesii roots also led to upregulated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and phospho-cAMP response element-binding protein (p-CREB) in the hippocampal region. These findings suggest that the extract of D. mariesii roots, along with its active constituents, may offer neuroprotective effects against AD. Consequently, there is potential for the development of the extract of D. mariesii roots and its active constituents as effective therapeutic or preventative agents for AD.
Keywords: Aβ aggregation; Aβ production; ethanol extract of D. mariesii roots; flavonoids; scopolamine-induced memory impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
6-Methyluracil derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S69-71. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150694. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639718
-
In vivo and in vitro evaluation of the osteogenic potential of Davallia mariesii T. Moore ex Baker.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 10;264:113126. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113126. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32763416
-
Protective Effects of Compounds from Cimicifuga dahurica against Amyloid Beta Production in Vitro and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Vivo.J Nat Prod. 2020 Feb 28;83(2):223-230. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00543. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 32031796
-
Panax ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer's disease.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Oct;42(4):401-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.12.008. Epub 2018 Jan 12. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 30337800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Phenolic Constituents from Drynariae Rhizoma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 13;17(8):1061. doi: 10.3390/ph17081061. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204166 Free PMC article.
-
Active Compounds of Panax ginseng in the Improvement of Alzheimer's Disease and Application of Spatial Metabolomics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 26;17(1):38. doi: 10.3390/ph17010038. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracalvariosseous administration of donepezil microspheres protects against cognitive impairment by virtue of long-lasting brain exposure in mice.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 14;14(17):6708-6725. doi: 10.7150/thno.100986. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg. Z. Psychiatr. Psych. Gerichtl. Med. 1907;64:146–168.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

