URB937 Prevents the Development of Mechanical Allodynia in Male Rats with Trigeminal Neuralgia
- PMID: 38004491
- PMCID: PMC10675761
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111626
URB937 Prevents the Development of Mechanical Allodynia in Male Rats with Trigeminal Neuralgia
Abstract
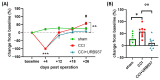
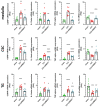
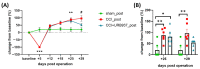
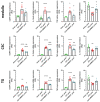
Cannabinoids are proposed for alleviating neuropathic pain, but their use is limited by cannabimimetic side effects. The inhibition of the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the degrading enzyme of the endocannabinoid anandamide, has received attention as an alternative to cannabinoids in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Here, we investigated the effect of URB937, a blood-brain barrier impermeant FAAH inhibitor, on experimentally induced mechanical allodynia in an animal model of trigeminal neuralgia. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to chronic constriction injury of the infraorbital nerve (IoN-CCI); operated animals were treated sub-chronically with URB937 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle before or after trigeminal mechanical allodynia establishment. We also assayed mRNA expression levels of the pain neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and cytokines in the medulla, cervical spinal cord, and trigeminal ganglion ipsilateral to IoN-CCI using rt-PCR. URB937 treatment prevented the development of mechanical allodynia and IoN-CCI-induced changes in mRNA expression levels of CGRP and cytokines in the evaluated areas. When administered after allodynia development, URB937 prevented IoN-CCI-induced changes in CGRP and cytokine gene expression; this was not associated with a significant abrogation of the mechanical allodynia. These findings suggest that URB937 may counteract, but not reverse, the development of allodynia in trigeminal neuralgia. Further research is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: FAAH inhibitor; inflammation; pain; trigeminal neuralgia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the peripheral FAAH inhibitor, URB937, in animal models of acute and chronic migraine.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Jan;147:105157. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105157. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 33129939
-
Alterations in endocannabinoid tone following chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: effects of endocannabinoid deactivation inhibitors targeting fatty-acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase in comparison to reference analgesics following cisplatin treatment.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Jan;67(1):94-109. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23127915 Free PMC article.
-
Brain permeant and impermeant inhibitors of fatty-acid amide hydrolase suppress the development and maintenance of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain without producing tolerance or physical dependence in vivo and synergize with paclitaxel to reduce tumor cell line viability in vitro.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Apr;142:267-282. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30739035 Free PMC article.
-
CGRP receptor blockade by MK-8825 alleviates allodynia in infraorbital nerve-ligated rats.Eur J Pain. 2015 Feb;19(2):281-90. doi: 10.1002/ejp.616. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Eur J Pain. 2015. PMID: 25370954
-
Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Improves Depressive-Like Behaviors Independent of Its Peripheral Antinociceptive Effects in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain.Anesth Analg. 2019 Aug;129(2):587-597. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003563. Anesth Analg. 2019. PMID: 29863609
Cited by
-
Endocannabinoid Hydrolase Inhibitors: Potential Novel Anxiolytic Drugs.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jun 11;18:2143-2167. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S462785. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38882045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Psychotropic Drug for the Treatment of Trigeminal Pain: Salvinorin A.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;17(12):1619. doi: 10.3390/ph17121619. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicity and Toxicokinetics of a Four-Week Repeated Gavage of Levamisole in Male Beagle Dogs: A Good Laboratory Practice Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;17(1):141. doi: 10.3390/ph17010141. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guirguis-Blake J., Kelly C. Are Opioids Effective in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain? Am. Fam. Physician. 2007;75:999–1001. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

