Quercetin as a Therapeutic Product: Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Action and Clinical Applications-A Review
- PMID: 38004496
- PMCID: PMC10674654
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16111631
Quercetin as a Therapeutic Product: Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Action and Clinical Applications-A Review
Abstract
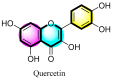
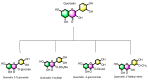
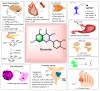
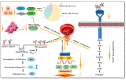
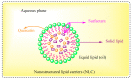
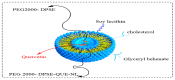
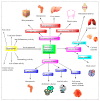
Quercetin is the major polyphenolic flavonoid that belongs to the class called flavanols. It is found in many foods, such as green tea, cranberry, apple, onions, asparagus, radish leaves, buckwheat, blueberry, broccoli, and coriander. It occurs in many different forms, but the most abundant quercetin derivatives are glycosides and ethers, namely, Quercetin 3-O-glycoside, Quercetin 3-sulfate, Quercetin 3-glucuronide, and Quercetin 3'-metylether. Quercetin has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, antiviral, and antibacterial effects. It is found to be beneficial against cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, neuro-degenerative diseases, allergy asthma, peptic ulcers, osteoporosis, arthritis, and eye disorders. In pre-clinical and clinical investigations, its impacts on various signaling pathways and molecular targets have demonstrated favorable benefits for the activities mentioned above, and some global clinical trials have been conducted to validate its therapeutic profile. It is also utilized as a nutraceutical due to its pharmacological properties. Although quercetin has several pharmacological benefits, its clinical use is restricted due to its poor water solubility, substantial first-pass metabolism, and consequent low bioavailability. To circumvent this limited bioavailability, a quercetin-based nanoformulation has been considered in recent times as it manifests increased quercetin uptake by the epithelial system and enhances the delivery of quercetin to the target site. This review mainly focuses on pharmacological action, clinical trials, patents, marketed products, and approaches to improving the bioavailability of quercetin with the use of a nanoformulation.
Keywords: flavonoids; lipid nanoparticles; nanoformulation; quercetin; therapeutic profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aucoin M., Cooley K., Saunders P.R., Cardozo V., Remy D., Cramer H., Abad C.N., Hannan N. The effect of quercetin on the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections in humans: A rapid review. Adv. Integr. Med. 2020;7:247–251. doi: 10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

