Tailoring Risperidone-Loaded Glycethosomal In Situ Gels Using Box-Behnken Design for Treatment of Schizophrenia-Induced Rats via Intranasal Route
- PMID: 38004501
- PMCID: PMC10675145
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112521
Tailoring Risperidone-Loaded Glycethosomal In Situ Gels Using Box-Behnken Design for Treatment of Schizophrenia-Induced Rats via Intranasal Route
Abstract
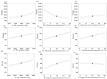
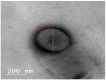
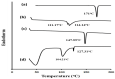
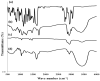
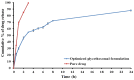
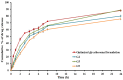
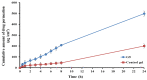
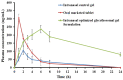
Schizophrenic patients often face challenges with adherence to oral regimens. The study aimed to highlight the potentiality of intranasal ethanol/glycerin-containing lipid-nanovesicles (glycethosomes) incorporated into in situ gels for sustaining anti-psychotic risperidone (RS) release. The Box-Behnken Design (BBD) was followed for in vitro characterization. Glycethosomal-based in situ gels were examined by physical, ex vivo, and in vivo investigations. The ethanol impact on minimizing the vesicle size (VS) and enhancing the zeta potential (ZP) and entrapment efficiency (EE%) of nanovesicles was observed. Glycerin displayed positive action on increasing VS and ZP of nanovesicles, but reduced their EE%. After incorporation into various mucoadhesive agent-enriched poloxamer 407 (P407) in situ gels, the optimized gel containing 20% P407 and 1% hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose-K4M (HPMC-K4M) at a 4:1 gel/glycethosomes ratio showed low viscosity and high spreadability with acceptable pH, gel strength, and mucoadhesive strength ranges. The ethanol/glycerin mixture demonstrated a desirable ex vivo skin permeability of RS through the nasal mucosa. By pharmacokinetic analysis, the optimized gel showed eight-fold and three-fold greater increases in RS bioavailability than the control gel and marketed tablet, respectively. Following biochemical assessments of schizophrenia-induced rats, the optimized gel boosted the neuroprotective, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory action of RS in comparison to other tested preparations. Collectively, the intranasal RS-loaded glycethosomal gel offered a potential substitute to oral therapy for schizophrenic patients.
Keywords: ELISA assay; ex vivo permeation; glycethosomal vesicles; in situ intranasal gel; pharmacokinetic study; risperidone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Nano-Bilosomal In Situ Gels Containing Anti-Psychotic Clozapine for Treatment of Schizophrenia: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;17(10):1404. doi: 10.3390/ph17101404. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459043 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Glycerosomal pH Triggered In Situ Gelling System to Ameliorate the Nasal Delivery of Sulpiride for Pediatric Psychosis.Gels. 2024 Sep 23;10(9):608. doi: 10.3390/gels10090608. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39330210 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal In Situ Gel of Apixaban-Loaded Nanoethosomes: Preparation, Optimization, and In Vivo Evaluation.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 May 4;22(4):147. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02020-y. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 33948767
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Niosomal in situ Nasal Gel of a Serotonin Receptor Agonist, Buspirone Hydrochloride for the Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018;6(1):69-78. doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180130105919. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29380709
-
Buspirone Hydrochloride Loaded In Situ Nanovesicular Gel as an Anxiolytic Nasal Drug Delivery System: In Vitro and Animal Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Mar 4;20(3):134. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-1211-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 30830481
Cited by
-
Plant-Based Nanovesicular Gel Formulations Applied to Skin for Ameliorating the Anti-Inflammatory Efficiency.Gels. 2024 Aug 10;10(8):525. doi: 10.3390/gels10080525. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39195054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-A Key Excipient in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):784. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060784. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified Phospholipid Vesicular Gel for Transdermal Drug Delivery: The Influence of Glycerin and/or Ethanol on Their Lipid Bilayer Fluidity and Penetration Characteristics.Gels. 2025 May 13;11(5):358. doi: 10.3390/gels11050358. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40422378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Nano-Bilosomal In Situ Gels Containing Anti-Psychotic Clozapine for Treatment of Schizophrenia: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;17(10):1404. doi: 10.3390/ph17101404. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459043 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical studies of Veitchia arecina Becc. leaves with evaluation of in-vitro, in-vivo anti-inflammatory, and wound healing properties in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01802-1. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40488788
References
-
- World Health Organization . Report of the International Pilot Study of Schizophrenia. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1973.
-
- Uttl L., Petrasek T., Sengul H., Svojanovska M., Lobellova V., Vales K., Radostova D., Tsenov G., Kubova H., Mikulecka A. Chronic MK-801 application in adolescence and early adulthood: A spatial working memory deficit in adult Long-Evans rats but no changes in the hippocampal NMDA receptor subunits. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:42. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gener T., Campo A.T., Alemany-González M., Nebot P., Delgado-Sallent C., Chanovas J., Puig M.V. Serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A and dopamine D2 receptors strongly influence prefronto-hippocampal neural networks in alert mice: Contribution to the actions of risperidone. Neuropharmacology. 2019;158:107743. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107743. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

