Gene and Cellular Therapies for Leukodystrophies
- PMID: 38004502
- PMCID: PMC10675548
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112522
Gene and Cellular Therapies for Leukodystrophies
Abstract
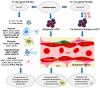
Leukodystrophies are a heterogenous group of inherited, degenerative encephalopathies, that if left untreated, are often lethal at an early age. Although some of the leukodystrophies can be treated with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, not all patients have suitable donors, and new treatment strategies, such as gene therapy, are rapidly being developed. Recent developments in the field of gene therapy for severe combined immune deficiencies, Leber's amaurosis, epidermolysis bullosa, Duchenne's muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy, have paved the way for the treatment of leukodystrophies, revealing some of the pitfalls, but overall showing promising results. Gene therapy offers the possibility for overexpression of secretable enzymes that can be released and through uptake, allow cross-correction of affected cells. Here, we discuss some of the leukodystrophies that have demonstrated strong potential for gene therapy interventions, such as X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD), and metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD), which have reached clinical application. We further discuss the advantages and disadvantages of ex vivo lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy, an approach for targeting microglia-like cells or rendering cross-correction. In addition, we summarize ongoing developments in the field of in vivo administration of recombinant adeno-associated viral (rAAV) vectors, which can be used for direct targeting of affected cells, and other recently developed molecular technologies that may be applicable to treating leukodystrophies in the future.
Keywords: adeno-associated viral vectors; gene therapy; lentiviral vectors; leukodystrophies; stem cell transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene therapy for the leukodystrophies: From preclinical animal studies to clinical trials.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Jul;21(4):e00443. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00443. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 39276676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene therapy for leukodystrophies.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Apr 15;20(R1):R42-53. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr142. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21459776 Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in leukodystrophies.Handb Clin Neurol. 2024;204:355-366. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-99209-1.00017-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39322389 Review.
-
Recent Advancements in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Leukodystrophies.Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2021 Apr;37:100876. doi: 10.1016/j.spen.2021.100876. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33892849 Review.
-
An update on clinical, pathological, diagnostic, and therapeutic perspectives of childhood leukodystrophies.Expert Rev Neurother. 2020 Jan;20(1):65-84. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2020.1699060. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Expert Rev Neurother. 2020. PMID: 31829048 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction of Griscelli Syndrome Type 2 causing mutations in the RAB27A gene with CRISPR/Cas9.Turk J Biol. 2024 Jul 31;48(5):290-298. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2705. eCollection 2024. Turk J Biol. 2024. PMID: 39474038 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy for the leukodystrophies: From preclinical animal studies to clinical trials.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Jul;21(4):e00443. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00443. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 39276676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

