Novel Transethosomal Gel Containing Miconazole Nitrate; Development, Characterization, and Enhanced Antifungal Activity
- PMID: 38004517
- PMCID: PMC10675164
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112537
Novel Transethosomal Gel Containing Miconazole Nitrate; Development, Characterization, and Enhanced Antifungal Activity
Abstract
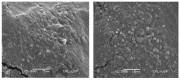
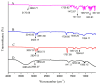
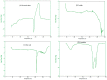
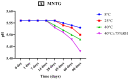
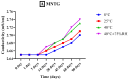
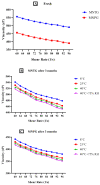
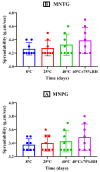
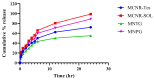
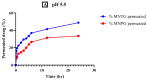
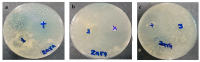
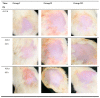
Miconazole nitrate (MCNR) is a BCS class II antifungal drug with poor water solubility. Although numerous attempts have been made to increase its solubility, formulation researchers struggle with this significant issue. Transethosomes are promising novel nanocarriers for improving the solubility and penetration of drugs that are inadequately soluble and permeable. Thus, the objective of this study was to develop MCNR-loaded transethosomal gel in order to enhance skin permeation and antifungal activity. MCNR-loaded transethosomes (MCNR-TEs) were generated using the thin film hydration method and evaluated for their zeta potential, particle size, polydispersity index, and entrapment efficiency (EE%). SEM, FTIR, and DSC analyses were also done to characterize the optimized formulation of MCNR-TEs (MT-8). The optimized formulation of MCNR-TEs was incorporated into a carbopol 934 gel base to form transethosomal gel (MNTG) that was subjected to ex vivo permeation and drug release studies. In vitro antifungal activity was carried out against Candida albicans through the cup plate technique. An in vivo skin irritation test was also performed on Wistar albino rats. MT-8 displayed smooth spherical transethosomal nanoparticles with the highest EE% (89.93 ± 1.32%), lowest particle size (139.3 ± 1.14 nm), polydispersity index (0.188 ± 0.05), and zeta potential (-18.1 ± 0.10 mV). The release profile of MT-8 displayed an initial burst followed by sustained release, and the release data were best fitted with the Korsmeyer-Peppas model. MCNR-loaded transethosomal gel was stable and showed a non-Newtonian flow. It was found that ex vivo drug permeation of MNTG was 48.76%, which was significantly higher than that of MNPG (plain gel) (p ≤ 0.05) following a 24-h permeation study. The prepared MCNR transethosomal gel exhibited increased antifungal activity, and its safety was proven by the results of an in vivo skin irritation test. Therefore, the developed transethosomal gel can be a proficient drug delivery system via a topical route with enhanced antifungal activity and skin permeability.
Keywords: carbopol 934; ex vivo permeation; gel; health care; in vitro antifungal activity; miconazole nitrate; skin irritation test; transethosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In Vivo Evaluation of Miconazole-Nitrate-Loaded Transethosomal Gel Using a Rat Model Infected with Candida albicans.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;17(5):546. doi: 10.3390/ph17050546. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794118 Free PMC article.
-
Transethosomes of Econazole Nitrate for Transdermal Delivery: Development, In-vitro Characterization, and Ex-vivo Assessment.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018;6(3):171-179. doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180813122102. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30101725
-
Fabrication and Evaluation of Voriconazole Loaded Transethosomal Gel for Enhanced Antifungal and Antileishmanial Activity.Molecules. 2022 May 23;27(10):3347. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103347. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630825 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Efficacy of Berberine Hydrochloride-loaded Transethosomal Gel System in Treating Dermatophytosis Caused by Trichophyton rubrum in ex-vivo, in-vitro and in-vivo Models.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16(3):412-422. doi: 10.2174/2589977515666230726151456. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37496248
-
Tioconazole-Loaded Transethosomal Gel Using Box-Behnken Design for Topical Applications: In Vitro, In Vivo, and Molecular Docking Approaches.Gels. 2023 Sep 21;9(9):767. doi: 10.3390/gels9090767. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37754448 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and evaluation of nanoemulsion gel loaded with bioactive extract of Cucumis melo var. agrestis: A novel approach for enhanced skin permeability and antifungal activity.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e35069. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35069. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170221 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery Research-Focus on Nanoformulations.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 16;16(6):817. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060817. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Exploitation of Sodium Deoxycholate-Stabilized Nano-Vesicular Gel for Ameliorating the Antipsychotic Efficiency of Sulpiride.Gels. 2024 Mar 31;10(4):239. doi: 10.3390/gels10040239. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667658 Free PMC article.
-
Transethosomes: A Comprehensive Review of Ultra-Deformable Vesicular Systems for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jan 17;26(1):41. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-03035-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 39825015 Review.
-
In Vivo Evaluation of Miconazole-Nitrate-Loaded Transethosomal Gel Using a Rat Model Infected with Candida albicans.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;17(5):546. doi: 10.3390/ph17050546. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonina F., Montenegro L. Vehicle effects on in vitro heparin release and skin penetration from different gels. Int. J. Pharm. 1994;102:19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(94)90035-3. - DOI
-
- Mulani H., Bhise K.S. QbD Approach in the formulation and evaluation of Miconazole Nitrate loaded ethosomal cream-o-gel. Int. Res. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017;8:1–13.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

