Exploiting Pharma 4.0 Technologies in the Non-Biological Complex Drugs Manufacturing: Innovations and Implications
- PMID: 38004525
- PMCID: PMC10674941
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112545
Exploiting Pharma 4.0 Technologies in the Non-Biological Complex Drugs Manufacturing: Innovations and Implications
Abstract
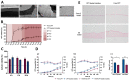
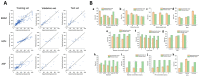
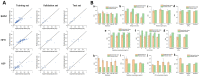
The pharmaceutical industry has entered an era of transformation with the emergence of Pharma 4.0, which leverages cutting-edge technologies in manufacturing processes. These hold tremendous potential for enhancing the overall efficiency, safety, and quality of non-biological complex drugs (NBCDs), a category of pharmaceutical products that pose unique challenges due to their intricate composition and complex manufacturing requirements. This review attempts to provide insight into the application of select Pharma 4.0 technologies, namely machine learning, in silico modeling, and 3D printing, in the manufacturing process of NBCDs. Specifically, it reviews the impact of these tools on NBCDs such as liposomes, polymeric micelles, glatiramer acetate, iron carbohydrate complexes, and nanocrystals. It also addresses regulatory challenges associated with the implementation of these technologies and presents potential future perspectives, highlighting the incorporation of digital twins in this field of research as it seems to be a very promising approach, namely for the optimization of NBCDs manufacturing processes.
Keywords: Pharma 4.0; digital twins; in silico modeling; machine learning; non-biological complex drugs; three-dimensional (3D) printing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Non-biological Complex Drugs (NBCDs): Complex Pharmaceuticals in Need of Individual Robust Clinical Assessment Before Any Therapeutic Equivalence Decision.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 23;7:590527. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.590527. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33330550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Therapeutic Equivalence for the Follow-On Version of Intravenously Administered Non-Biological Complex Drugs.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020 Aug;59(8):995-1004. doi: 10.1007/s40262-020-00889-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 32328977 Review.
-
3D Printing Methods for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Opportunity and Challenges.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(42):4949-4956. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666181206121701. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30520367 Review.
-
The EU regulatory landscape of non-biological complex drugs (NBCDs) follow-on products: Observations and recommendations.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019 May 15;133:228-235. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.03.029. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 30953753 Review.
-
Digital manufacturing of advanced materials: challenges and perspective.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2019 Sep;28:49-62. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2019. PMID: 32831619 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancing Regulatory Oversight of Medical Device Trials to Align with Clinical Drug Standards in the European Union.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;18(6):876. doi: 10.3390/ph18060876. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Accelerating the Discovery and Development of Nanomedicine.Pharm Res. 2024 Dec;41(12):2289-2297. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03798-9. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 39623144
-
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Innovation: From Drug Discovery to Clinical Trials.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 25;18(6):788. doi: 10.3390/ph18060788. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharma M., Sehrawat R., Luthra S., Daim T., Bakry D. Moving Towards Industry 5.0 in the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Sector: Challenges and Solutions for Germany. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022:1–18. doi: 10.1109/TEM.2022.3143466. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

