Rapid and Widespread Distribution of Intranasal Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells throughout the Brain Potentially via the Perivascular Pathway
- PMID: 38004556
- PMCID: PMC10675165
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112578
Rapid and Widespread Distribution of Intranasal Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells throughout the Brain Potentially via the Perivascular Pathway
Abstract
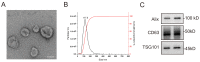
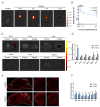
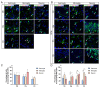
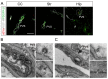
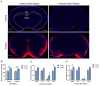
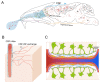
Intranasal administration is a promising strategy to enhance the delivery of the sEVsomes-based drug delivery system to the central nervous system (CNS). This study aimed to explore central distributive characteristics of mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (MSC-sEVs) and underlying pathways. Here, we observed that intranasal MSC-sEVs were rapidly distributed to various brain regions, especially in the subcortex distant from the olfactory bulb, and were absorbed by multiple cells residing in these regions. We captured earlier transportation of intranasal MSC-sEVs into the perivascular space and found an increase in cerebrospinal fluid influx after intranasal administration, particularly in subcortical structures of anterior brain regions where intranasal sEVs were distributed more significantly. These results suggest that the perivascular pathway may underlie the rapid and widespread central delivery kinetics of intranasal MSC-sEVs and support the potential of the intranasal route to deliver MSC-sEVs to the brain for CNS therapy.
Keywords: distribution; extracellular vesicles; intranasal administration; perivascular space.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Curative Effect of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Small Extracellular Vesicles in Treating Osteoarthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 16;16:8185-8202. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S336062. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34938076 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal delivery of BDNF-loaded small extracellular vesicles for cerebral ischemia therapy.J Control Release. 2023 May;357:1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.03.033. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 36958402
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-105-5p via small extracellular vesicles to rejuvenate senescent nucleus pulposus cells and attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 13;12(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02362-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33985571 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles in the treatment of human diseases: Progress and prospect.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Jan 26;13(1):49-63. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i1.49. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33584979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perivascular and Perineural Pathways Involved in Brain Delivery and Distribution of Drugs after Intranasal Administration.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Nov 12;11(11):598. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11110598. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31726721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal delivery of imaging agents to the brain.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 19;14(13):5022-5101. doi: 10.7150/thno.98473. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39267777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal Administration of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Has Therapeutic Effect in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Cells. 2025 Jul 30;14(15):1172. doi: 10.3390/cells14151172. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801605 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization strategies for mesenchymal stem cell-based analgesia therapy: a promising therapy for pain management.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jul 18;15(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03828-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39020426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery after human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBM-MSCs)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) treatment in post-MCAO rats requires repeated handling.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 21;19(10):e0312298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312298. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39432503 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as precision therapeutics for psychiatric conditions: targeting interactions among neuronal, glial, and immune networks.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1454306. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1454306. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

