Photodynamic Therapy-Induced Anti-Tumor Immunity: Influence Factors and Synergistic Enhancement Strategies
- PMID: 38004595
- PMCID: PMC10675361
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112617
Photodynamic Therapy-Induced Anti-Tumor Immunity: Influence Factors and Synergistic Enhancement Strategies
Abstract
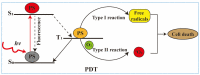
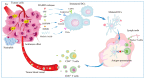
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an approved therapeutic procedure that exerts cytotoxic activity towards tumor cells by activating photosensitizers (PSs) with light exposure to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). Compared to traditional treatment strategies such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, PDT not only kills the primary tumors, but also effectively suppresses metastatic tumors by activating the immune response. However, the anti-tumor immune effects induced by PDT are influenced by several factors, including the localization of PSs in cells, PSs concentration, fluence rate of light, oxygen concentration, and the integrity of immune function. In this review, we systematically summarize the influence factors of anti-tumor immune effects mediated by PDT. Furthermore, an update on the combination of PDT and other immunotherapy strategies are provided. Finally, the future directions and challenges of anti-tumor immunity induced by PDT are discussed.
Keywords: combination therapy; influence factors; innate immunity; photodynamic therapy; specific immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Togsverd-Bo K., Sandberg C., Helsing P., Mørk G., Wennberg A.M., Wulf H.C., Haedersdal M. Cyclic photodynamic therapy delays first onset of actinic keratoses in renal transplant recipients: A 5-year randomized controlled trial with 12-month follow-up. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022;36:E946–E948. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18374. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barreca M., Ingarra A.M., Raimondi M.V., Spanò V., Piccionello A.P., De Franco M., Menilli L., Gandin V., Miolo G., Barraja P., et al. New tricyclic systems as photosensitizers towards triple negative breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2022;45:806–821. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01414-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1207600/the National Key R&D Program of China
- T2293750/the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- T2293753/the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- XSQD-202023003/the Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars
- 2019-I2M-5-061/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

