Advances in Polymeric Micelles: Responsive and Targeting Approaches for Cancer Immunotherapy in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 38004600
- PMCID: PMC10675796
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112622
Advances in Polymeric Micelles: Responsive and Targeting Approaches for Cancer Immunotherapy in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
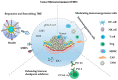
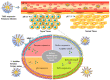
In recent years, to treat a diverse array of cancer forms, considerable advancements have been achieved in the field of cancer immunotherapies. However, these therapies encounter multiple challenges in clinical practice, such as high immune-mediated toxicity, insufficient accumulation in cancer tissues, and undesired off-target reactions. To tackle these limitations and enhance bioavailability, polymer micelles present potential solutions by enabling precise drug delivery to the target site, thus amplifying the effectiveness of immunotherapy. This review article offers an extensive survey of recent progress in cancer immunotherapy strategies utilizing micelles. These strategies include responsive and remodeling approaches to the tumor microenvironment (TME), modulation of immunosuppressive cells within the TME, enhancement of immune checkpoint inhibitors, utilization of cancer vaccine platforms, modulation of antigen presentation, manipulation of engineered T cells, and targeting other components of the TME. Subsequently, we delve into the present state and constraints linked to the clinical utilization of polymeric micelles. Collectively, polymer micelles demonstrate excellent prospects in tumor immunotherapy by effectively addressing the challenges associated with conventional cancer immunotherapies.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; polymeric micelles; responsive delivery systems; targeted drug delivery; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Drug Delivery Based on Polymeric Micelles for Precision Cancer Therapy: Strategies and Prospects.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 11;12(2):417. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020417. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision nanomedicine: navigating the tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy and targeted drug delivery.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 3;24(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02357-z. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40457437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Micelles in Cancer Immunotherapy.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1220. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051220. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Prodrug Micelles Imitate Mild Heat Effects to Reshape Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy.ACS Nano. 2024 Feb 20;18(7):5632-5646. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c11186. Epub 2024 Feb 12. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38344992 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted nanomedicines remodeling immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Dec;12(12):4327-4347. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.11.001. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36561994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Personalized nanovaccines for treating solid cancer metastases.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Nov 28;17(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01628-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39609851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Drug Delivery Based on Polymeric Micelles for Precision Cancer Therapy: Strategies and Prospects.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 11;12(2):417. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020417. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROTAC Delivery Strategies for Overcoming Physicochemical Properties and Physiological Barriers in Targeted Protein Degradation.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 9;17(4):501. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040501. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioneering Advances and Innovative Applications of Mesoporous Carriers for Mitochondria-Targeted Therapeutics.Br J Biomed Sci. 2024 Nov 18;81:13707. doi: 10.3389/bjbs.2024.13707. eCollection 2024. Br J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 39624468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cohen E.E.W., Bell R.B., Bifulco C.B., Burtness B., Gillison M.L., Harrington K.J., Le Q.T., Lee N.Y., Leidner R., Lewis R.L., et al. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) J. Immunother. Cancer. 2019;7:184. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0662-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

