Anti-Obesity Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Progress and Challenges
- PMID: 38004612
- PMCID: PMC10674714
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112635
Anti-Obesity Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Progress and Challenges
Abstract
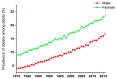
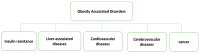
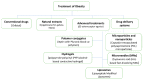
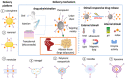
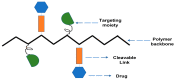
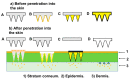
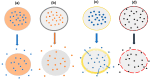
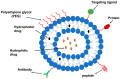
Obesity has reached an epidemic proportion in the last thirty years, and it is recognized as a major health issue in modern society now with the possibility of serious social and economic consequences. By the year 2030, nearly 60% of the global population may be obese or overweight, which emphasizes a need for novel obesity treatments. Various traditional approaches, such as pharmacotherapy and bariatric surgery, have been utilized in clinical settings to treat obesity. However, these methods frequently show the possibility of side effects while remaining ineffective. There is, therefore, an urgent need for alternative obesity treatments with improved efficacy and specificity. Polymeric materials and chemical strategies are employed in emerging drug delivery systems (DDSs) to enhance therapy effectiveness and specificity by stabilizing and controlling the release of active molecules such as natural ingredients. Designing DDSs is currently a top priority research objective with an eye towards creating obesity treatment approaches. In reality, the most recent trends in the literature demonstrate that there are not enough in-depth reviews that emphasize the current knowledge based on the creation and design of DDSs for obesity treatment. It is also observed in the existing literature that a complex interplay of different physical and chemical parameters must be considered carefully to determine the effectiveness of the DDSs, including microneedles, for obesity treatment. Additionally, it is observed that these properties depend on how the DDS is synthesized. Although many studies are at the animal-study stage, the use of more advanced DDS techniques would significantly enhance the development of safe and efficient treatment approaches for obese people in the future. Considering these, this review provides an overview of the current anti-obesity treatment approaches as well as the conventional anti-obesity therapeutics. The article aims to conduct an in-depth discussion on the current trends in obesity treatment approaches. Filling in this knowledge gap will lead to a greater understanding of the safest ways to manage obesity.
Keywords: active molecules; anti-obesity drugs; microneedles; nanoparticles; natural ingredients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Implantable sustained-release drug delivery systems: a revolution for ocular therapeutics.Int Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul;43(7):2575-2588. doi: 10.1007/s10792-023-02637-x. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Int Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36715956 Review.
-
Polymeric Carriers for Controlled Drug Delivery in Obesity Treatment.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Dec;30(12):974-989. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.09.004. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31668904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of pancreatic lipase inhibition in obesity treatment: mechanisms and challenges towards current insights and future directions.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 Mar;49(3):492-506. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01729-1. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40016558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral delivery of Kaempferia parviflora's methoxyflavones via nanostructured lipid carriers: Its effect on obesity and dyslipidemia treatment".Int J Pharm X. 2025 Jun 11;9:100345. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100345. eCollection 2025 Jun. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40584401 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Therapeutic Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Treating High-fat Diet-induced Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy based on GEO Datasets, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(38):3054-3070. doi: 10.2174/0113816128311226240730080713. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39171590
-
Succinic Acid Improves the Metabolism of High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice and Promotes White Adipose Browning.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 8;16(22):3828. doi: 10.3390/nu16223828. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599615 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanin7 in adipose tissue remodeling and its impact on metabolic health.Mol Metab. 2025 Jul;97:102168. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102168. Epub 2025 May 12. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40368161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau D.C., Douketis J.D., Morrison K.M., Hramiak I.M., Sharma A.M., Ur E., Obesity Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert P. 2006 Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the management and prevention of obesity in adults and children [summary] CMAJ. 2007;176:S1–S13. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.061409. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO . The World Health Report 2000: Health Systems: Improving Performance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2000.
-
- WHO Obesity and Overweight. Jun 9, 2021. [(accessed on 2 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

