Bioactive ZnO Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, Characterization and Potential Antimicrobial Applications
- PMID: 38004613
- PMCID: PMC10675506
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112634
Bioactive ZnO Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, Characterization and Potential Antimicrobial Applications
Abstract
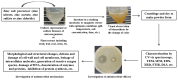
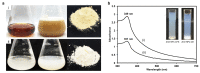
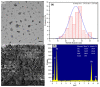
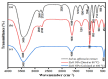
In recent years, biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) have gained tremendous attention because of their safe and non-toxic nature and distinctive biomedical applications. A diverse range of microbes (bacteria, fungi and yeast) and various parts (leaf, root, fruit, flower, peel, stem, etc.) of plants have been exploited for the facile, rapid, cost-effective and non-toxic synthesis of ZnONPs. Plant extracts, microbial biomass or culture supernatant contain various biomolecules including enzymes, amino acids, proteins, vitamins, alkaloids, flavonoids, etc., which serve as reducing, capping and stabilizing agents during the biosynthesis of ZnONPs. The biosynthesized ZnONPs are generally characterized using UV-VIS spectroscopy, TEM, SEM, EDX, XRD, FTIR, etc. Antibiotic resistance is a serious problem for global public health. Due to mutation, shifting environmental circumstances and excessive drug use, the number of multidrug-resistant pathogenic microbes is continuously rising. To solve this issue, novel, safe and effective antimicrobial agents are needed urgently. Biosynthesized ZnONPs could be novel and effective antimicrobial agents because of their safe and non-toxic nature and powerful antimicrobial characteristics. It is proven that biosynthesized ZnONPs have strong antimicrobial activity against various pathogenic microorganisms including multidrug-resistant bacteria. The possible antimicrobial mechanisms of ZnONPs are the generation of reactive oxygen species, physical interactions, disruption of the cell walls and cell membranes, damage to DNA, enzyme inactivation, protein denaturation, ribosomal destabilization and mitochondrial dysfunction. In this review, the biosynthesis of ZnONPs using microbes and plants and their characterization have been reviewed comprehensively. Also, the antimicrobial applications and mechanisms of biosynthesized ZnONPs against various pathogenic microorganisms have been highlighted.
Keywords: ZnONPs; antimicrobial applications; antimicrobial mechanisms; biosynthesis; characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications of Gold Nanoparticles: Current Status and Future Prospects.Biomedicines. 2025 May 13;13(5):1184. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051184. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the effectiveness of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles in controlling multidrug-resistant clinical bacteria.Indian J Microbiol. 2023 Mar;63(1):65-72. doi: 10.1007/s12088-022-01048-3. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Indian J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37188233 Free PMC article.
-
Rhamnella gilgitica functionalized green synthesis of ZnONPs and their multiple therapeutic properties.Microsc Res Tech. 2022 Jun;85(6):2338-2350. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24090. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Microsc Res Tech. 2022. PMID: 35294072
-
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pomegranate Fruit Peel and Solid Coffee Grounds vs. Chemical Method of Synthesis, with Their Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties Investigation.Molecules. 2022 Feb 12;27(4):1236. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041236. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209025 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis and Potential Antibacterial Applications of Bioactive Silver Nanoparticles: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 15;14(4):742. doi: 10.3390/polym14040742. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles: therapeutic implications for Parkinson's disease.Biosci Rep. 2024 Nov 27;44(11):BSR20241102. doi: 10.1042/BSR20241102. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39501749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial, antifungal, and antibiofilm activities of biogenic zinc nanoparticles against pathogenic microorganisms.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 14;15:1545119. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1545119. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40727704 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Synthesis of Bioactive Silver Nanoparticles Using Brevibacillus sp. MAHUQ-41 and Their Potential Application Against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens Listeria monocytogenes and Yersinia enterocolitica.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jun 30;16(7):241. doi: 10.3390/jfb16070241. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40710455 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications of Gold Nanoparticles: Current Status and Future Prospects.Biomedicines. 2025 May 13;13(5):1184. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051184. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lyophilized Polyvinyl Alcohol and Chitosan Scaffolds Pre-Loaded with Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles for Tissue Regeneration.Molecules. 2024 Aug 14;29(16):3850. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163850. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urge S.K., Dibaba S.T., Gemta A.B. Green Synthesis Method of ZnO Nanoparticles using Extracts of Zingiber officinale and Garlic Bulb (Allium sativum) and Their Synergetic Effect for Antibacterial Activities. J. Nanomater. 2023;2023:7036247.
-
- Kumar R., Vinoth S., Baskar V., Arun M., Gurusaravanan P. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated by Dictyota dichotoma endophytic fungi and its photocatalytic degradation of fast green dye and antibacterial applications. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022;151:337–344. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2022.03.016. - DOI
-
- Akter S., Huq M.A. Biologically rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Sphingobium sp. MAH-11T and their antibacterial activity and mechanisms investigation against drug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020;48:672–682. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2020.1730390. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

