The Effect of Probiotics in a Milk Replacer on Leukocyte Differential Counts, Phenotype, and Function in Neonatal Dairy Calves
- PMID: 38004631
- PMCID: PMC10673549
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112620
The Effect of Probiotics in a Milk Replacer on Leukocyte Differential Counts, Phenotype, and Function in Neonatal Dairy Calves
Abstract
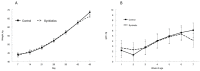
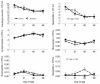
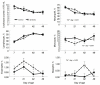
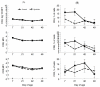
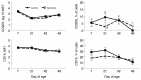
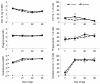
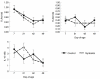
Probiotics have been investigated for many health benefits; however, few studies have been performed to determine the effects of oral probiotics on peripheral blood and respiratory immune cells in cattle. Our objectives were to determine changes in health and growth status, differential blood cell counts and function, and blood and lung cell function using flow cytometry and PCR in dairy calves fed a milk replacer with (PRO, N = 10) or without (CON, N = 10) the addition of probiotics to the milk replacer and dry rations from birth to weaning. Performance and clinical scores were not different between the treatment groups. Treatment-by-day interactions for peripheral blood leukocyte populations differed in cell number and percentages. A greater percentage of leukocytes expressed the cell surface markers CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11b, and CD205 on d 21 in CON animals. Lung lavages were performed on five animals from each treatment group on d 52. There were no differences between treatment groups for the expression of cytokines and Toll-Like Receptors as measured using Polymerase Chain Reaction, possibly due to the small sample size. Oral probiotics appear to affect peripheral blood immune cells and function. Their effect on overall calf health remains to be determined.
Keywords: bovine; dairy calves; leukocyte; probiotic; respiratory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probiotics in milk replacer affect the microbiome of the lung in neonatal dairy calves.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1298570. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1298570. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38249465 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementing neonatal Jersey calves with a blend of probiotic bacteria improves the pathophysiological response to an oral Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium challenge.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Aug;103(8):7351-7363. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17480. Epub 2020 May 29. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32475670
-
Short communication: Effects of increasing protein and energy in the milk replacer with or without direct-fed microbial supplementation on growth and performance of preweaned Holstein calves.J Dairy Sci. 2014 Nov;97(11):7212-9. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-7000. Epub 2014 Sep 6. J Dairy Sci. 2014. PMID: 25200791 Clinical Trial.
-
Different methods of eubiotic feed additive provision affect the health, performance, fermentation, and metabolic status of dairy calves during the preweaning period.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Apr 12;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03239-y. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35413974 Free PMC article.
-
A 100-Year Review: Calf nutrition and management.J Dairy Sci. 2017 Dec;100(12):10151-10172. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13062. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 29153160 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into microbial compositions of the respiratory tract of neonatal dairy calves in a longitudinal probiotic trial through 16S rRNA sequencing.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1499531. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1499531. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39845057 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

